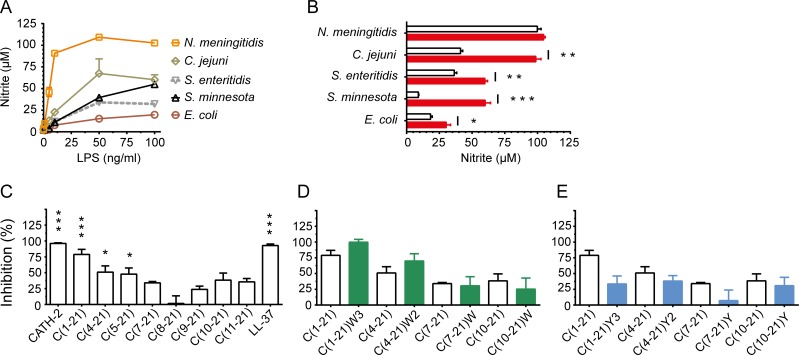
Fig 5. CATH-2 analog neutralization of LPS-induced macrophage nitric oxide production.
Nitric oxide production by HD11 cells stimulated with LPS (50 to 100 ng/ml) pre-incubated with CATH-2 derived peptides (20 μM). Nitric oxide (NO) production was measured in supernatants after 24 h incubation using the Griess assay. Amino acid substitutions: W3, [F2W, F5W, F12W]; W2, [F5W, F12W]; W, [F12W]; Y3, [F2Y, F5Y, F12Y]; Y2, [F5Y, F12Y]; Y, [F12Y]. a Dose-dependent production of NO by HD11 cells exposed to different sources of LPS. b CATH-2 significantly inhibited NO production induced by all tested LPS (100 ng/ml) sources, except wild-type Neisseria meningitidis LPS; bars indicate LPS-induced NO production in the absence (closed) and presence (open) of CATH-2 peptide. c Inhibition of S. minnesota LPS-induced (50 ng/ml) NO production by truncated CATH-2 analogs. Production of LPS-induced NO by HD11 cells was significantly reduced in the presence of C(1–21) and N-terminally truncated C(1–21) analogs up to 17 amino acid residues. d, e Phe/Trp substitution enhanced inhibition of active peptides C(1–21) and C(4–21), whereas Phe/Tyr substitution abrogated inhibition of LPS-induced NO production by these peptides. Data from 3 to 4 independent experiments; means ± SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.