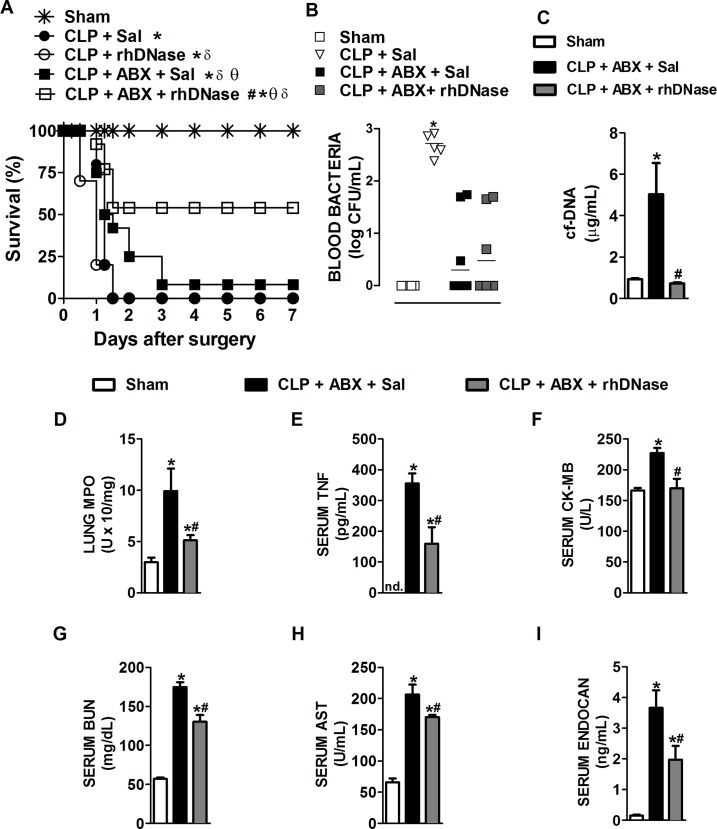
Fig 2. NETs degradation by rhDNase treatment associated with antibiotic therapy improves the outcome of CLP-induced sepsis.
Mice were subjected to sham surgery or CLP-induced severe sepsis. (A) Mice were post-treated with saline or rhDNase (10 mg/kg, sc. - 1 h after the surgery and every 8 h thereafter), associated or not with ertapenem antibiotic (ABX—30 mg/kg, sc. - 1 h after the surgery and every 12 h thereafter for 48 h). The survival rates were evaluated over 7 days. * p < 0.05 compared with the sham group; δ p < 0.05 compared with the CLP + Sal group; θ p < 0.05 compared with the CLP + rhDNase group; # p < 0.05 compared with the CLP + ABX + Sal group (Mantel-Cox log-rank test, n = 10 per experimental group). (B-I) Mice were post-treated with saline or rhDNase (10 mg/kg, sc. - 1 and 8 h after the surgery), associated or not with ertapenem antibiotic (30 mg/kg, sc. - 1 h after the surgery). Twelve hours after sepsis induction, blood bacterial levels (B), serum concentration of cf-DNA, (C), MPO in lung tissue (D) and serum concentrations of TNF (E), CK-MB (F), BUN (G), AST (H) and endocan (I) were quantified. The data are reported as the mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05 compared with the sham group; # p < 0.05 compared with the CLP + ABX + Sal group (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test, n = 5 per experimental group); bacteria: the horizontal bars represent the median (Mann-Whitney U test, n = 5–7 per experimental group).