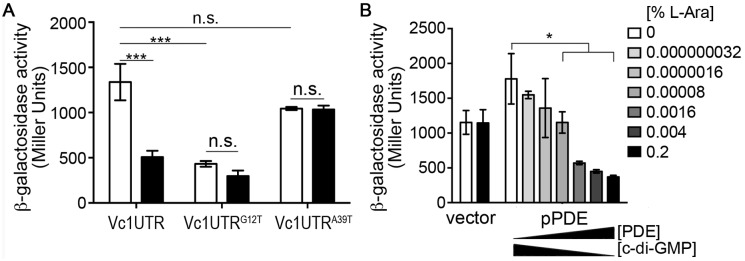
Fig 5. Lowering intracellular c-di-GMP reduces Vc1-dependent gene expression.
β-galactosidase activity of V. cholerae strains with chromosomal, translational fusions of E. coli lacZ to the gbpA 5’ UTR with wild type Vc1, Vc1G12T, or Vc1A39T, with transcription initiation under the control of the constitutive PlacUV5 promoter: PlacUV5-Vc1UTR-lacZ, PlacUV5-Vc1UTRG12T-lacZ, PlacUV5-Vc1UTRA39T-lacZ, respectively [38]. Each reporter strain carried pPDE and was grown without arabinose (wild-type c-di-GMP level; white bars) or with 0.2% arabinose (reduced c-di-GMP; black bars). (B) Dose response analysis using the PlacUV5-Vc1UTR-lacZ reporter strain, with vector or pPDE, grown in rich medium with a range of arabinose concentrations. Increasing PDE production corresponds with decreasing intracellular c-di-GMP. (A and B) Measurements of β-galactosidase activity were done with at least three independent biological samples, and the means and standard error are shown. * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001, n.s. = not significant by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test.