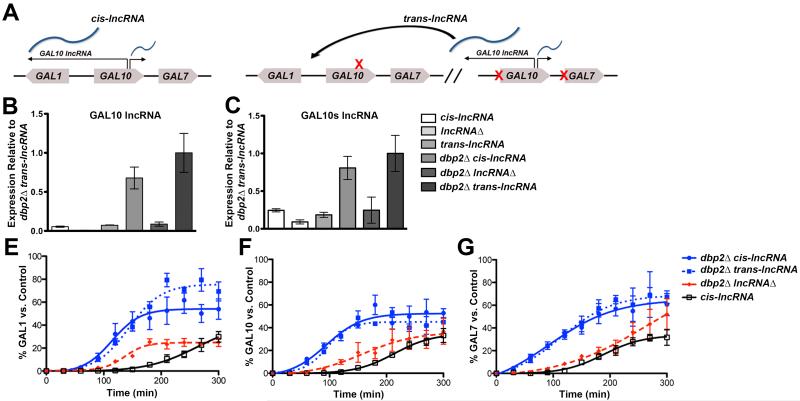
Figure 1. GAL lncRNAs function in trans to promote induction of the GAL cluster genes.
(A) A schematic of “cis-lncRNAs” and “trans-lncRNAs” at the GAL cluster. (B-C) The trans-lncRNA strain expresses the GAL lncRNAs at similar levels to cis-encoded strains. Levels of the antisense GAL10 lncRNA (B) and GAL10s lncRNA (C) were assayed in wild type, lncRNAΔ, dbp2Δ, dbp2Δ lncRNAΔ, trans-lncRNA and dbp2Δ trans-lncRNAΔ cells by strand-specific RT-qPCR (ssRT-qPCR) as described (Beck et al., 2014) using cells grown in repressive (+glucose) conditions and primers listed in Table S5. Results are presented as the mean of 3 biological replicates relative to ACT1 with S.E.M. (D-F) Graphical representation of GAL gene induction of isogenic wild type, dbp2Δ, and dbp2Δ lncRNAΔ and dbp2Δ “trans-lncRNA” strains. Transcriptional induction of GAL1 (D), GAL10 (E) and GAL7 (F) transcripts during a shift from repressive (+glucose) to activated conditions (+galactose) was assayed by Northern blotting, quantified with respect to sCR1, and plotted as a percentage of a fully induced wild type “control” as previously described (Cloutier et al., 2013). Results are presented as the mean with SEM of three biological replicates. Also see Figure S1.