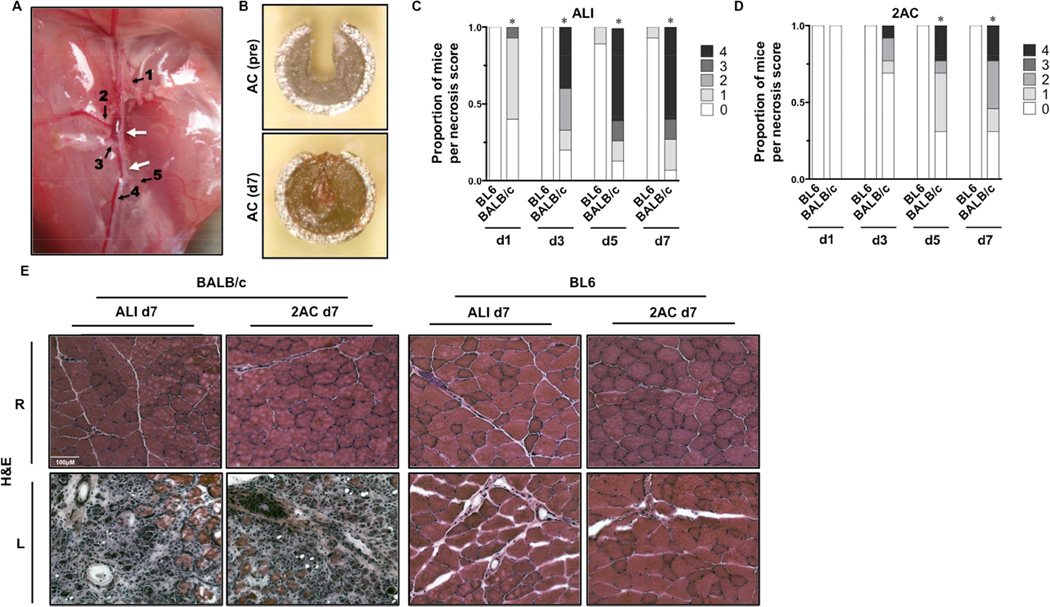
Figure 1. Tissue pathology after subacute femoral artery occlusion with two ameroid constrictors.
Acute hindlimb ischemia (ALI) or sub-acute femoral artery occlusion using 2ACs was performed in BL6 and BALB/c mice, and animals were monitored for 7-days (ALI N=16 per strain; 2AC, N=8 BL6 – N=13 BALB/c). A, Representative image and schematic of sites of ligation/resection for ALI or 2AC placement on the femoral artery. Arrows indicate sites of constrictor placement or resection. 1 Lateral Circumflex Femoral. 2 Proximal Caudal Femoral. 3 Superficial Caudal Epigastric. 4 Saphenous. 5 Popliteal.B Ex vivo image of an AC after removal at day 7, demonstrating complete occlusion. C, Distribution of limb necrosis scores during the week of ischemia (d1, d3, d5, d7) induced by ALI in BL6 and BALB/c mice. *P<0.05 vs. day matched BL6. D, Distribution of limb necrosis scores during the week of ischemia (d1, d3, d5, d7) induced by 2AC in BL6 and BALB/c mice. *P<0.05 vs. day matched BL6. E, Representative H&E sections demonstrating TA morphology 7 days after ALI and 2AC surgery; R, right (non-surgical limb); L, left (surgical limb).