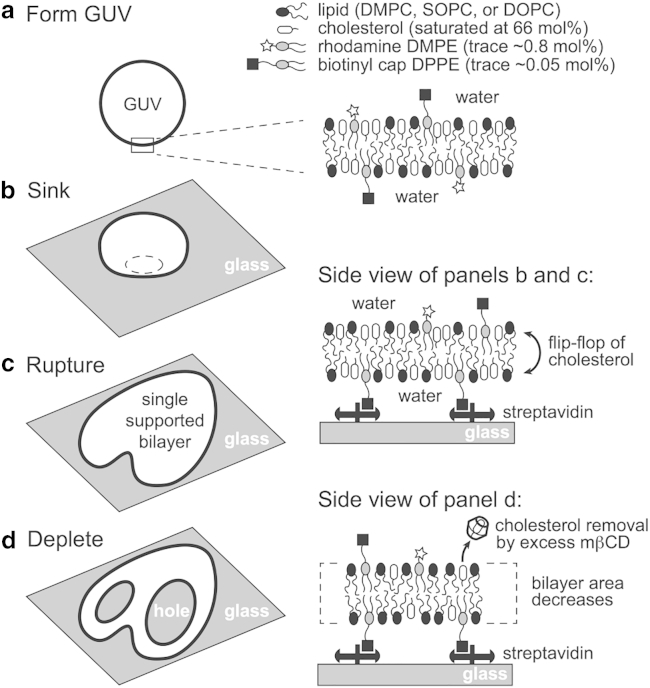
Figure 2.
Overview of the experimental procedure. (a) A GUV saturated with cholesterol at 66 mol % is produced via electroformation. (b) The GUV sinks to the bottom of the experimental chamber. (c) It then ruptures onto a streptavidin-functionalized glass coverslip, forming a heart-shaped SLB. Cholesterol flip-flop is rapid between the upper and lower leaflets of the fluid bilayer (39, 40, 41, 42). (d) mβCD is added to the chamber, where it selectively removes cholesterol from the SLB. Large holes form in the SLB as cholesterol is depleted, and the bilayer area decreases.