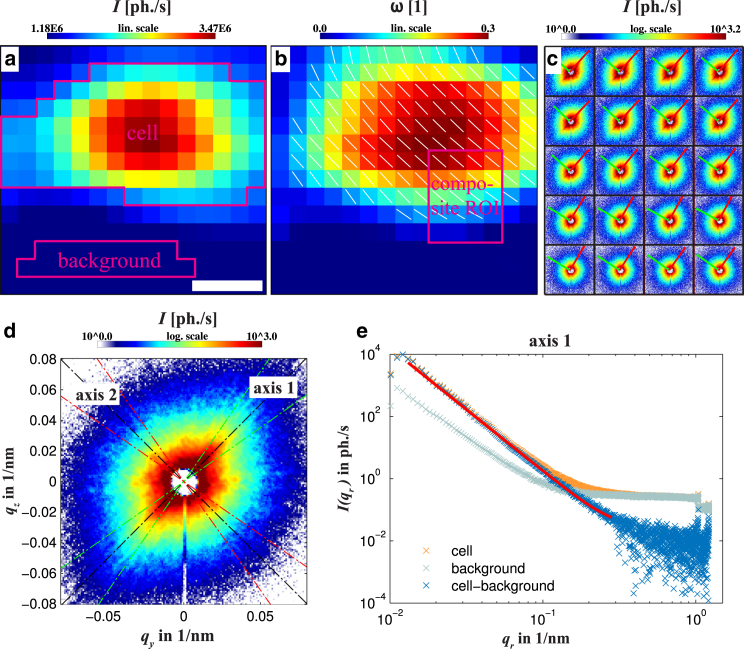
Figure 4.
(a) X-ray dark field image of a freeze-dried murine myoblast recorded with the micro-SAXS setup. Scale bar, 20 μm. (b) PCA result: White lines indicate the principal orientation axis. The anisotropy parameter ω (see Eq. 9) is color-coded. (c) Composite of the region marked in (b). Each diffraction pattern is cropped to a region of qr < 0.11 nm−1. The corresponding eigenvectors are scaled by their relative standard deviation and depicted as red and green arrows (for further explanations, see Analysis of Anisotropy in the Diffraction Patterns). (d) Average diffraction signal of the cell. The region taken into account is marked in (a). The two axes resulting from PCA indicate the principal directions of anisotropy, the directions of lowest and highest variance. (e) Averaged radial intensity profile of a segment ±10° around axis 1. Data are then fitted by a power law function following Eq. 4, resulting in b = −3.95 (axis 1) and b = −3.74 (axis 2), not shown. To see this figure in color, go online.