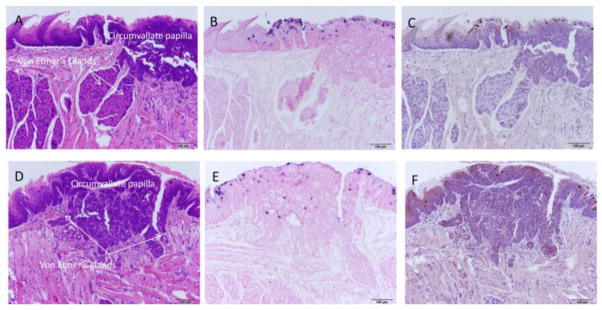
Fig. 4.
A–F Back of the tongue secondary lesions involved the circumvallate papilla and adjacent Von Ebner’s glands and exhibited marked dysplasia. A) H and E (100x) of a sagittal section of the caudodorsal tongue of animal 8-2R demonstrating florid pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia of the epithelium of the circumvallate papilla of the dorsal tongue adjacent to and extending into the duct of the serous lingual accessory salivary (Von Ebner’s) glands. Adjacent duct of the mucinous salivary gland is unaffected. B) ISH (100x) of an adjacent section demonstrating strong staining in the superficial epithelial cells, correlating with viral cytopathic effect seen on H&E section. C) IHC (100x) of an adjacent section showing capsid antigen presence in the same areas positive for MmuPV1 DNA. D) H and E (100x) of a sagittal section of the caudodorsal tongue of animal 10-2L demonstrating florid pseudocarcinomatous hyperplasia of the epithelium of the circumvallate papilla of the dorsal tongue adjacent to and extending into the duct of the serous lingual accessory salivary (Von Ebner’s) glands. Adjacent duct of the mucinous salivary gland is unaffected. E) ISH (100x) of an adjacent section demonstrating strong staining in the superficial epithelial cells, correlating with viral cytopathic effect seen on H&E section. F) IHC (100x) of an adjacent section showing capsid antigen presence in the same areas positive for MmuPV1 DNA.