Figure 3.
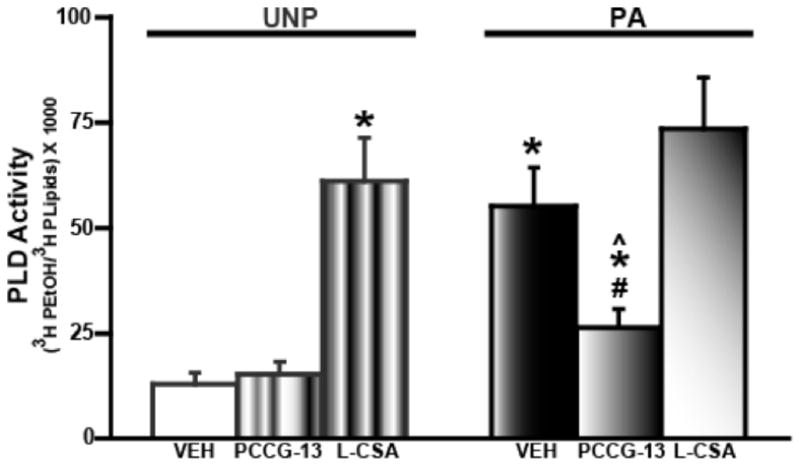
FPS increases and PLD-mGluR antagonist (PCCG-13) reduces amygdala PLD activity. PLD activity is expressed as a ratio of the amount of tritiated phosphatidyl ethanol (3H PEtOH) to total phospholipids (3H PLipids). PLD activity is significantly increased in the PA VEH (black bar) group compared to UNP VEH (white bar). The PLD-mGluR antagonist, PCCG-13, (2 μM) has no effect in the UNP group but decreases the PLD activity in amygdala from PA animals. The PLD-mGluR agonist, L-CSA, (100 μM) increases the PLD activity in the UNP group compared to UNP VEH group but not in the PA L-CSA group compared to PA VEH and UNP L-CSA groups. * denotes p<0.05 compared to UNP VEH control; # indicates p<0.05 compared to PA VEH control and ^ represents p<0.05 compared to UNP PCCG-13.
