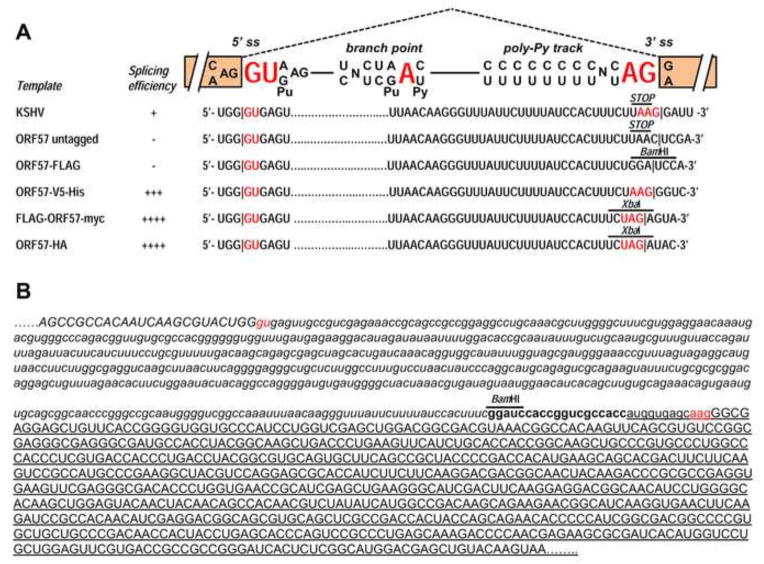
Fig. 3.
Sequence structure of the ORF57 intron 2 and its adjacent exons. (A) Diagram of an eukaryotic GU-AG intron and its important features (5′ splice site [5′ ss], branch point sequence, polypyrimidine track, and 3′ splice site [3′ ss]). Below the diagram are the ORF57 suboptimal intron 2 and its native 3′ splice site or an artificially created 3′ splice site derived from the cloning site of individual expression vectors. Stop indicates a stop codon UAA in the native ORF57 ORF. In addition to the 5′ splice site GU, the 3′ splice site AG, and the branch point A in red color, a nucleotide preceding the AG dinucleotide in a 3′ splice site is also colored in red to show its importance in selection of a 3′ splice site. (B) Partial sequence view of the chimeric ORF57-GFP fusion region, with exon sequences in uppercase, intron sequences in lowercase, ORF57 in italic, and vector in bold letters. The GFP sequences are underlined. The 5′ splice site GU and 3′ splice site AG and its preceding A are red colored. A BamHI site used for insertion of ORF57 ORF into the pEGFP-N1 vector is shown.