Figure 4.
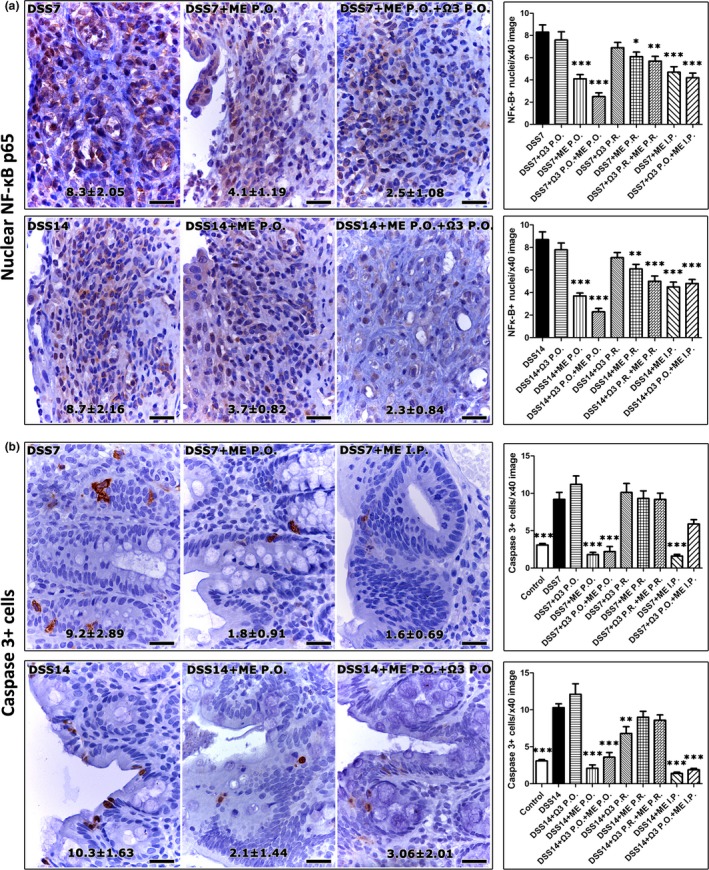
Mesna decreases the nuclear translocation of NF‐κΒ p65 in the DSS‐induced colonic ulcers and suppresses epithelial cell apoptosis in non‐ulcerated areas. (a) A fraction of the inflammatory cells populating the granulomatous tissue of ulcer beds show positive nuclear immunoreactivity for NF‐κΒ p65. The statistical comparison of histomorphometric counts suggests that Mesna reduces the number of cells with nuclear NF‐κΒ p65 at statistically significant levels. (b) Apoptotic epithelial cells have cytoplasmic cleaved caspase‐3. The analysis of morphometric counts shows that the effect of Mesna in reducing colonic epithelial cell apoptosis is significant. IHC, diaminobenzidine chromogen, haematoxylin counterstain. Scale bars: 25 μm. Numbers in the bottom of figures and the y‐axis of bar graphs depict the mean ± SEM of IHC‐labelled cells in high‐power magnification images. The asterisks indicate statistical significance between each experimental group with the control colitic rat group (black bar); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
