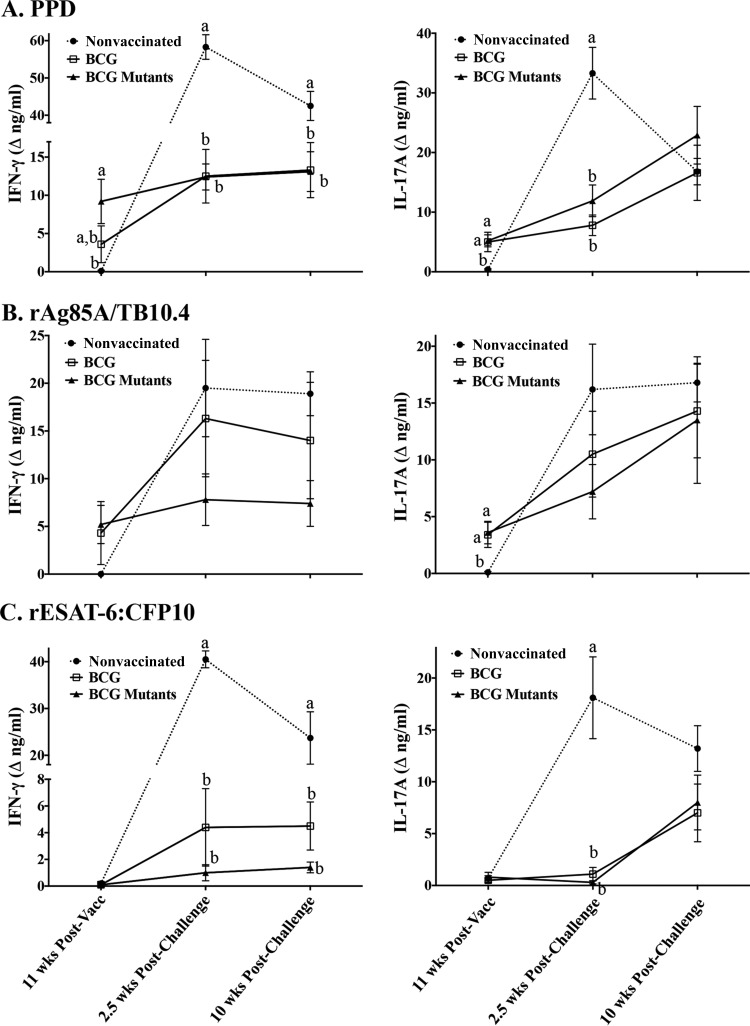
FIG 3.
IFN-γ and IL-17A responses to vaccination and subsequent challenge with virulent M. bovis. Treatment groups included nonvaccinated animals (n = 10), BCG-vaccinated animals (n = 9), and animals vaccinated with BCG mutants (i.e., BCG Δfdr8, BCG ΔleuCD Δpks16, BCG ΔmetA, and BCG ΔmmaA4) (n = 10). The virulent M. bovis strain 10-7428 was administered by aerosol to all calves 3.5 months after vaccination, and calves were euthanized 4.5 months after challenge (Table 1). Whole blood was collected into heparinized tubes and stimulated with 20 μg/ml M. bovis PPD (Lelystad; Prionics Ag) (A), 1 μg/ml rAg85A-rTB10.4 (B), 1 μg/ml rESAT-6:CFP10 (C), or medium alone (no stimulation) for 16 h at 39°C. Plasma was harvested for IFN-γ (left) and IL-17A (right) analyses using commercial ELISA kits (Bovigam [Prionics Ag] and bovine IL-17A ELISA VetSet [Kingfisher Biotech]). Data (mean ± SEM) are presented as the change in nanograms per milliliter (i.e., antigen stimulation minus medium alone) for each treatment group at the indicated time points relative to vaccination (Vacc) or challenge. a to c, different letters indicate that responses differ for the given time point (P < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple-comparison test).