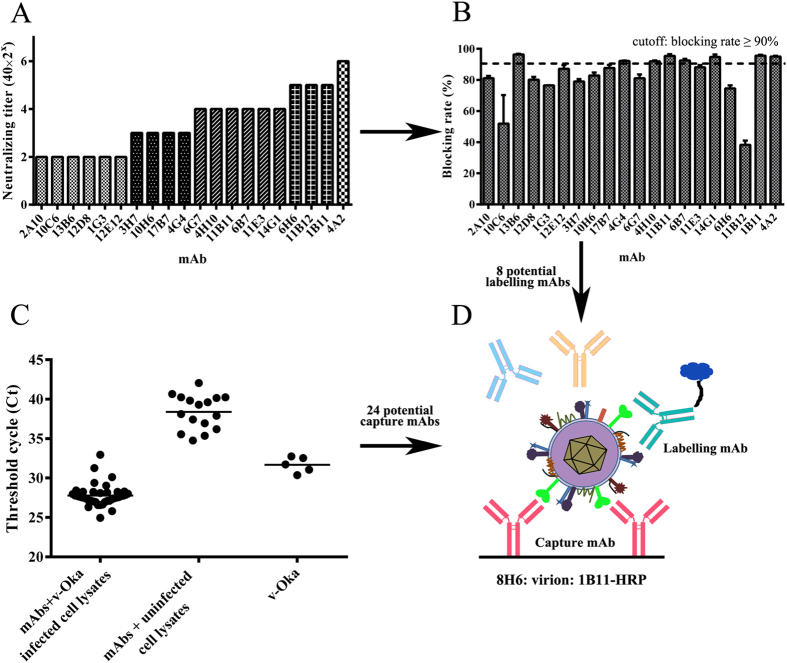
Figure 1. Establishment of a competitive sandwich ELISA to detect serum neutralizing antibody.
(A) 110 mAbs were obtained by immunization of mice with cell-free virus, purified VZV-gps and recombinant membrane proteins. All the mAbs were screened with an Elispot-based neutralization assay, and 20 complement-dependent neutralizing mAbs were obtained. (B) Blocking ELISA was performed with positive human serum. 8 neutralizing mAbs with a blocking rate greater than 90% were selected as potential labelling mAbs. (C) The ability of mAbs to capture VZV virions was evaluated by combining capture ELISA with quantitative real-time PCR. 24 mAbs in group I with threshold cycle (Ct) lower than average (27.78) were selected as potential capture mAbs. (D) Pairing experiment. Two rounds of pairing experiments were conducted to select a pair of mAbs for serum evaluation. In the first round of the pairing experiment, 192 combinations (24 × 8) were tested with one positive serum (FAMA titre = 1:16) and one negative serum (FAMA titre < 1:2), and 13 combinations were selected; in the second round of the pairing experiment, a panel of 20 human sera (12 positive sera (FAMA titre ≥ 1:8) and 8 negative sera (FAMA titre < 1:2)) were used for a correlation experiment. A pair of mAbs (8H6/1B11-HRP) were selected to established the competitive sandwich ELISA, which had a 100% coincidence rate with the FAMA test in the second pairing experiment.