Figure 2. Comparative accuracy of DBN models.
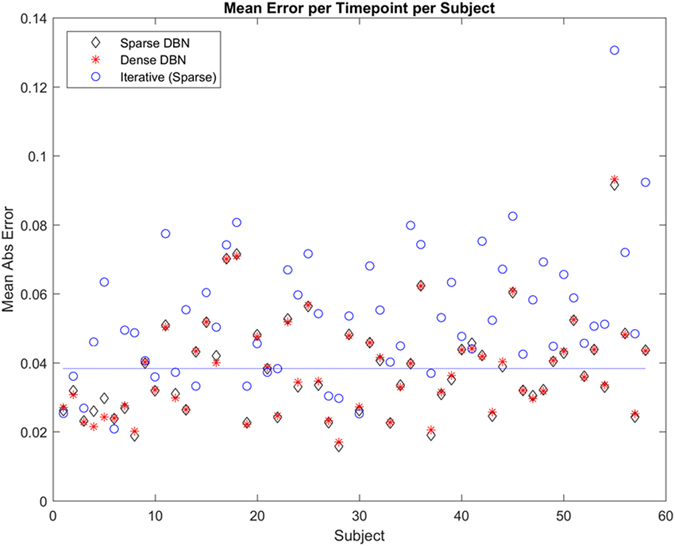
Accuracy in mean absolute error per subject is shown, where error is averaged across all bacteria taxa included in the Sparse network (Fig. 1). The Sparse DBN is simpler and performs better on subjects that are easier to predict (below empirical average of sparse networks’ mean absolute error, dashed blue line), while the Dense DBN (Supplemental Fig. 1) contains many more connections and performs better on subjects that are harder to predict (above the dashed blue line). This effect is significant when the two outliers (subjects #4 and #5) are removed (p = 0.045, t-test). Iterative prediction with the sparse network using only the first sample for each subject (blue circles) resulted in much larger average error per subject (p < 0.001, t-test).
