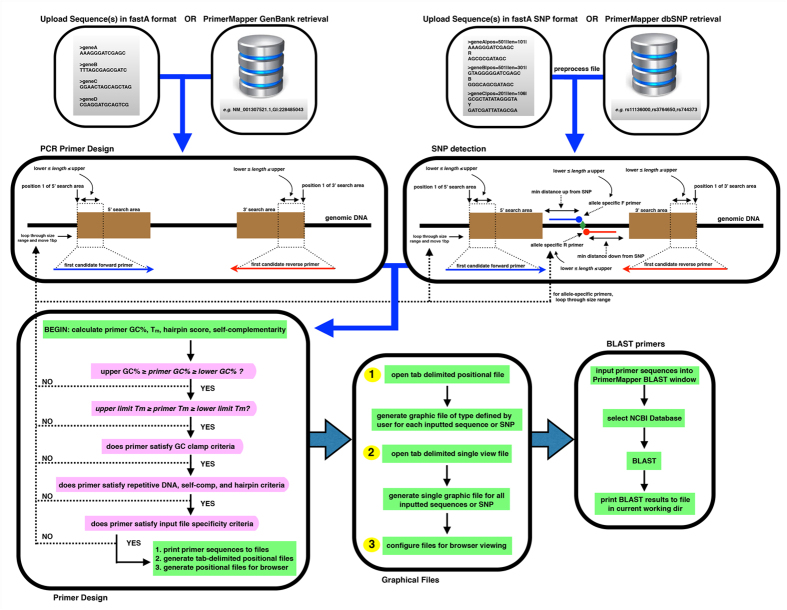
Figure 1. Flowchart of the PrimerMapper process.
Data can be uploaded into PrimerMapper from a local file or from NCBI’s GenBank22 or dbSNP23 databases. SNP sequence data is preprocessed by PrimerMapper prior to execution to collect the SNP position and type from the header field, and also to remove whitespace from the header field so as to preserve the entire sequence name. The user sets the various parameters for primer design for DNA sequence or SNP sequences such as primer maximum and minimum lengths, GC%, melting temperature (Tm), etc. PrimerMapper will then calculate hairpin and self-complementarity scores and only return primers whose scores meet specific thresholds. Repetitive sequence consisting of 5 or more mononucleotide repeats or more than 4 dinucleotide repeats is excluded from primer design by default (this can be changed by the user). Once all criteria are met, PrimerMapper will print the primer sequence and features to a file, and also generate files that mark the position and length of each primer within each sequence. These positional files are used to generate the graphical outputs for each sequence. For multiplex PCR reactions, it is useful to examine potential cross-complementarity between all primer pairs-to achieve this PrimerMapper can also implement a combinations without replacements algorithm (n choose k) for all primers to calculate cross-complementarity primer-dimer scores. Primer sequence(s) can then be inputted into the BLAST window to generate BLAST reports for each primer at a user-defined NCBI database.