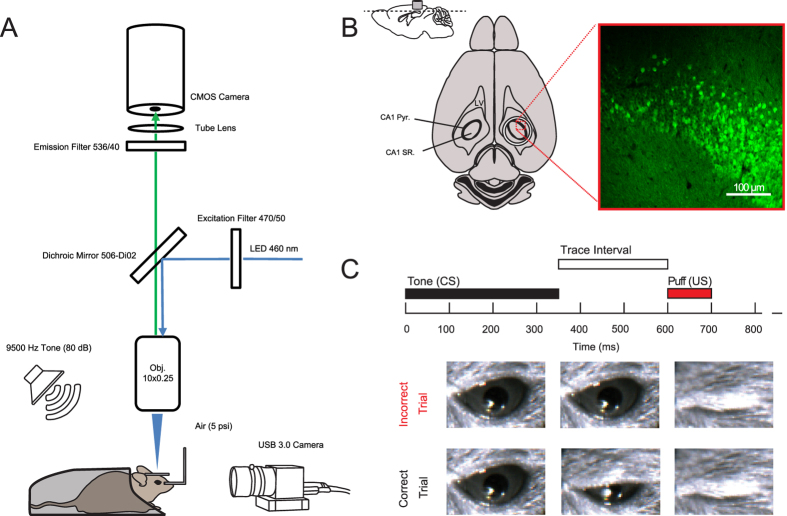
Figure 1. Experimental setup and behavioral design.
(A) Diagram of image acquisition system and behavioral apparatus. Ca2+ signals were captured using a CMOS camera and illumination was achieved using a 460 nm LED. Animals were positioned via a head holder under a 10X objective lens. Air puffs were delivered via a cannula directed at the right eye and a USB 3.0 camera was used to monitor eyelid position at 20 Hz. Auditory cues were delivered at 80 dB from a speaker positioned behind the animal. (B) Anatomical depiction of cannula placement and imaging plane. A representative confocal image from the animal analyzed in Figs 2, 3, 4, 5. Cannula is to scale: note that dorsal CA1 pyramidal cell layer below the cannula (CA1 pyr: stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum; LV, lateral ventricle). (C) Trace eye-blink paradigm. A 350 ms duration, 9500 Hz pure tone served as the conditioned stimulus (CS). The CS was followed by a 250 ms trace interval, which was followed by a 5 psi, 100 ms long, air puff to the eye that served as the unconditioned stimulus (US). Eyelid displacement was analyzed offline at the conclusion of the recording.