Figure 3. Molecular regulation of hyperglycemia-mediated carcinogenic promotion in head and neck cancer cells.
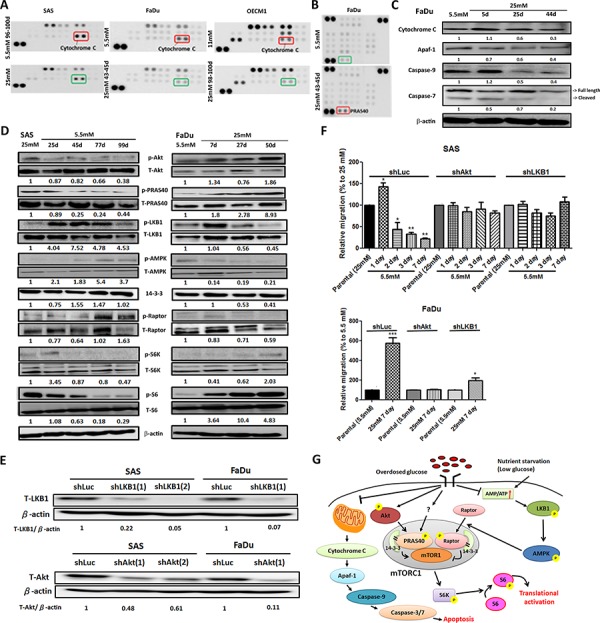
A. Mitochondrial redox sensor Cytochrome c is down-regulated in high-glucose culture condition in HNSCC cells using Human Cell Stress Antibody Array; B. Up-regulated expression of AKT/PKB substrate phospho-PRAS40 (T246) was shown in high-glucose treated FaDu cells using Human Phospho-Kinase Array; C. Western blot analysis showed Cytochrome c and its downstream molecules Apaf-1, caspase 9 and caspase 7 are down-regulated in FaDu cells cultured in high-glucose medium. The relative expression Cytochrome c, Apaf1, caspase 9 and cleaved caspase 7 was normalized with β-actin protein levels using Image J analysis software; D. Western blot analysis for molecules in Akt/AMPK-mTORC pathway showed differential expression in SAS and FaDu cells under various glycemic environments. The expression of active Akt, PRAS40 and mTORC1 downstream regulator p70S6K and its direct target S6 proteins were upregulated under high-glucose treatment while the increased active LKB1, AMPK and Raptor proteins were detected in SAS and FaDu cells treated with prolonged low-glucose condition. The activity of different proteins was defined as the ratios of phosphorylated protein expression to total protein levels using Image J analysis software; E. Western blot analysis showed successful establishment of Akt and LKB1 deficient SAS and FaDu cells using shRNA-mediated method. The knockdown efficiency was determined by Akt/LKB1 to β-actin protein expression ratio using Image J analysis software; F. Glycemia-mediated migration activity is abolished in Akt and LKB1 deficient SAS and FaDu cells. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM (N ≥ 3). ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05; G. Summary of glycemia-mediated molecular regulations in HNSCC cells.
