Figure 5. Activation of NF-κB by YBX1 functions downstream of IκBα degradation.
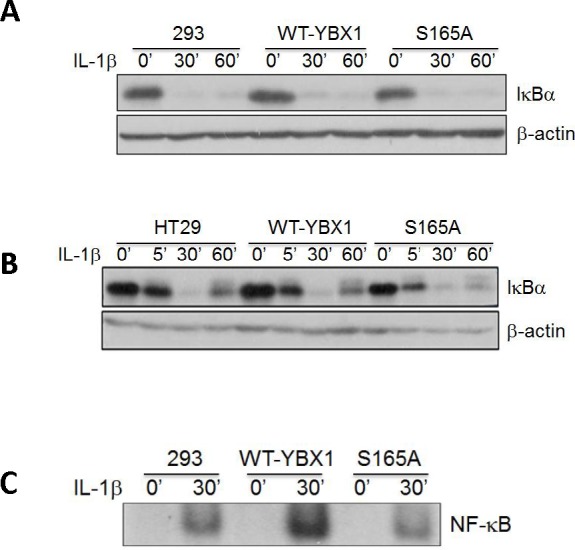

[A, B] Western Blot analyses, showing that overexpression of either WT-YBX1 or S165A-YBX1 did not affect the degradation of IκBα, suggesting that YBX1 functions downstream of IκBα degradation. C. EMSA assay, showing the overexpression of WT-YBX1 but not S165A-YBX1 enhanced NF-κB DNA binding ability upon IL-1β treatment, suggesting that phosphorylation of S165-YBX1 may enhance NF-κB DNA binding ability in nucleus. D. Immunofluorescence [IF] staining, showing the distribution of overexpressed WT-YBX1-Flag and S165A-YBX1-Flag in 293 cells. In untreated WT-YBX1 cells, YBX1 was located mainly in cytoplasm, but partly translocated into the nucleus after IL-1β treatment. However, YBX1 translocation was not observed in S165A-YBX1 mutant cells, before or after IL-1β treatment, suggesting that phosphorylation at S165 plays an important role in mediating the nuclear translocation of YBX1. DAPI was used for nuclear staining. E. IF experiment, showing that YBX1 co-localize with p65. IF experiment was carried out in 293, 293-WT-YBX1-Flag and S165A-YBX1-Flag stable cell lines. Anti-Flag was used to detect YBX1-Flag protein [green] and p65 antibody was used to detect endogenous P65 [red]. In 293 control cells, endogenous P65 is mainly located in cytoplasm while upon IL-1β treatment, P65 was observed in both cytoplasm and nucleus. No Flag-tagged YBX1 was observed in 293 cells. In WT-YBX1-Flag group, both Flag tagged YBX1 and endogenous p65 are located mainly in cytoplasm, but partly translocated into nuclear after IL-1β treatment and co-localized in nucleus. However, YBX translocation was not observed in S165A-YBX1-Flag cells, indicating that S165A eliminates YBX nuclear translocation ability. DAPI was used for nuclear staining.
