Figure 5. Molecular mechanisms to explain cancer preventive effects of cpKimchi (36 weeks after H. pylori infection).
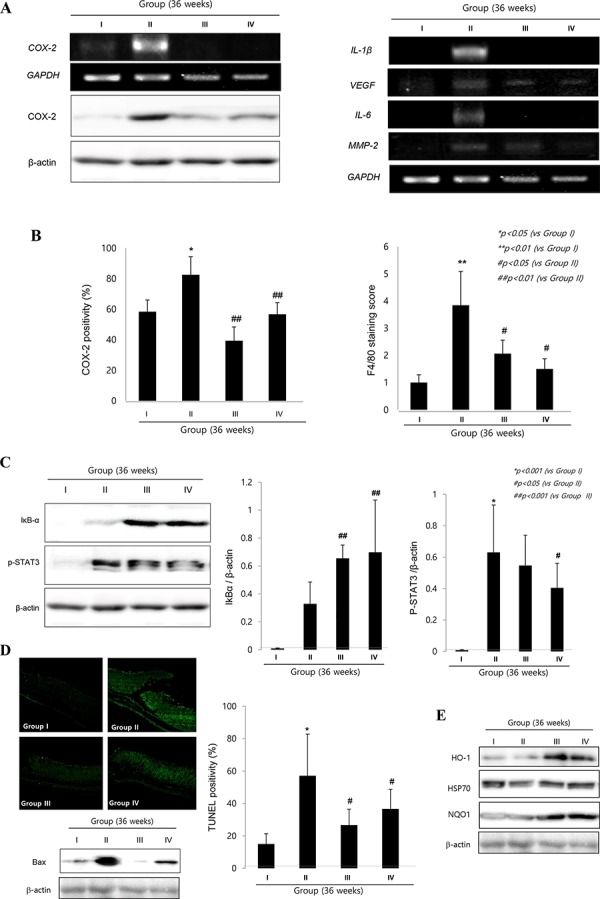
A. Changes of COX-2 and inflammatory mediators according to group On western blot and RT-PCR analysis of mucosal COX-2 expression, COX-2 was significantly increased after H. pylori infection, but its expressions were significantly decreased in group treated with cpKimchi. RT-PCR for IL-1β, VEGF, IL-6, MMP-2 was shown according to group and cpKimchi significantly decreased these H. pylori-induced inflammatory mediators. B. The immunohistochemical changes of COX-2 expressions and macrophage infiltrations according to group COX-2 and F/80 expressions were significantly increased in H. pylori infected control group. However, chronic 36 weeks intake of cpKimchi in drinking water significantly decreased COX-2 expressions as well as macrophage infiltration (p < 0.01). C. Western blot for p-STAT3 and IκB-α cpKimchi efficiently inhibited STAT3 activation and significantly inactivated IκB-α (p < 0.001). D. TUNEL staining for apoptosis and the expression of Bax In order to document the rejuvenating and restorative action of cpKimchi, TUNEL staining was done and apoptosis index was calculated according to group. Compatible with TUNEL, Bax expressions were significantly increased in Group II, but apparently decreased with cpKimchi administration. E. Western blot for Bax, NQO1, HO-1, and HSP70 according to group cpKimchi administration significantly increased NQO1 and HO-1 than control group II. HSP70 was significantly decreased in Group II, but preserved in Group III and IV.
