Figure 1. The Ras/ERK1–2 and RhoA/RhoA kinase signaling pathways and the HIF-1α/Pgp axis are more active in IGHV UM than M CLL cells.
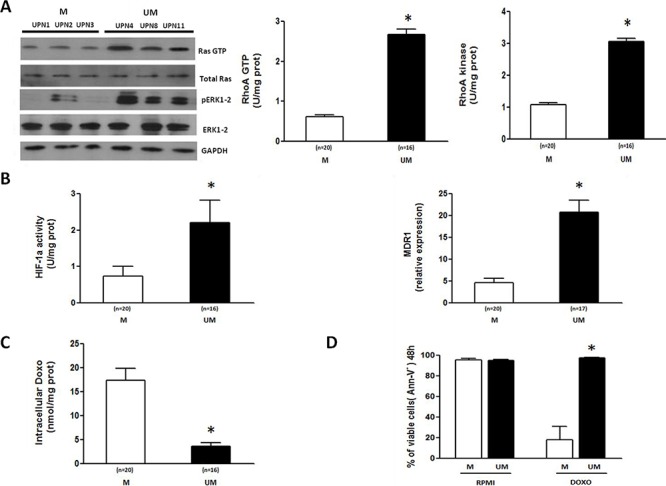
The activity of the Ras/ERK1–2 and RhoA/RhoA kinase signaling cascades and the HIF-1α/Pgp axis were measured in CLL cells isolated from the peripheral blood of IGHV M and UM patients after 24-hour ex vivo culture. A. Ras and ERK1–2 kinase activities were measured by Western Blot (WB) (left side). IGHV UM cells have a higher expression of the active forms of Ras (Ras GTP) and ERK1–2 (pERK1–2), than IGHV M cells. Results are from 3 representative experiments for both M and UM patients (UPN, unique patient number). RhoA GTP and RhoA Kinase activities were measured by ELISA assays (right side). IGHV UM cells have higher activities of RhoA GTP and RhoA Kinase compared to M cells (*p = 0.001). B. HIF-1α activity and MDR1 mRNA expression. IGHV UM cells have higher HIF-1α activity compared to M cells (*p = 0.002) after 24 hours of culture. At the same time-point, significantly higher MDR1 levels were observed in IGHV UM cells than in M cells (*p = 0.001). C. Intracellular Doxo accumulation. Significantly lower concentrations of Doxo were detected after 48-hour ex vivo exposure in IGHV UM than in M cells (*p = 0.001). D. Viability of CD19+/CD5+ cells was determined by Annexin-V (Ann-V) staining and cytofluorimetric analysis after 48-hour Doxo exposure. IGHV UM cells showed higher levels of viability than M cells (*p = 0.001). Results are from 7 experiments for both M and UM patients. In all panels, bars represent mean values ± SEM.
