Figure 5. SIM-mediated inhibition of HIF-1α activity and MDR1 gene expression improves Doxo-induced cytotoxicity.
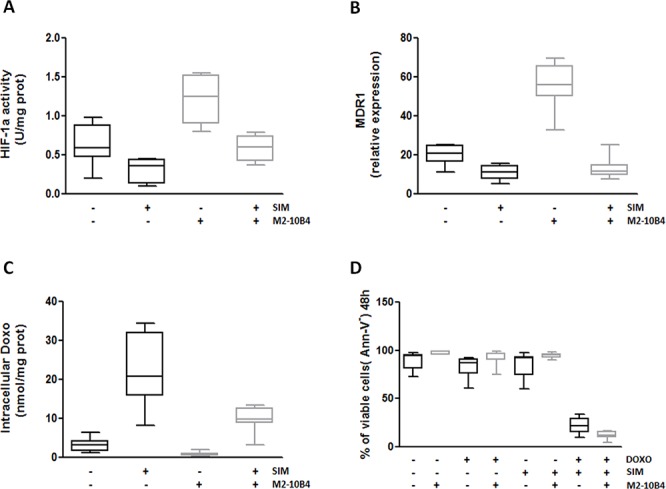
IGHV UM cells, cultured alone or in the presence of the murine stromal cell line M2–10B4, were exposed to 1 μM SIM. A. HIF-1α activity. The activity of HIF-1α was significantly increased by 24-hour co-culture with M2–10B4 SCs (p = 0.0007). SIM significantly reduced HIF-1α activity in IGHV UM cells, both in the absence (p = 0.003) and in the presence (p < 0.0001) of M2–10B4 SCs. B. MDR1 expression. Co-culture with M2–10B4 SCs significantly increased the levels of expression of MDR1 in IGHV UM cells (p < 0.0001). After 24-hour exposure to SIM, a significant decrease in MDR1 expression was observed in IGHV UM cells, both in the absence (p < 0.0001) and in the presence (p < 0.0001) of SCs. C. Doxo intracellular accumulation. The amount of intracellular Doxo in IGHV UM cells was significantly reduced by co-culture with M2–10B4 SCs (p = 0.010). SIM significantly increased 48-hour Doxo accumulation in IGHV UM cells cultured alone (p = 0.0026) or in the presence of SCs (p = 0.0002). D. Percentage of CD19+/CD5+ viable cells. IGHV UM cells were exposed to 1 μM Doxo, 1 μM SIM, and the combination SIM+Doxo for 48 hours, both in the absence and in the presence of M2–10B4 SCs. Cell viability was determined by Ann-V staining and cytofluorimetric analysis on CD19+/CD5+ cells. No decrease in viability was observed when IGHV UM cells were exposed to SIM and Doxo used alone (91% ± 2% and 90% ± 1% of CD19+/CD5+ viable cells, respectively). By contrast, a significant reduction in cell viability was induced by the combination SIM+Doxo, both in the absence (19, 5% ± 7% CD19+/CD5+ viable cells, p < 0.0001) and in the presence (10% ± 3% CD19+/CD5+ viable cells, p < 0.0001) of SCs. In panels A-D results are from 8 side-by-side experiments. Box and whiskers plot represent median values, first and third quartiles, and minimum and maximum values for each dataset.
