Figure 1. Honokiol inhibits leptin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration of breast cancer cells.
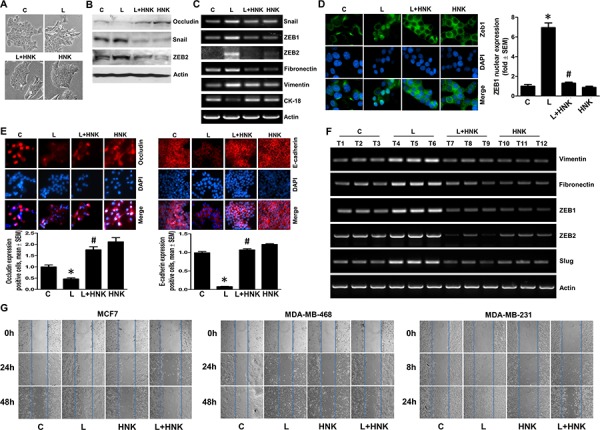
A. MCF7 cells were treated with leptin (L) (100 ng/ml) and/or Honokiol (HNK) (5 μM) as indicated. Vehicle treated cells are denoted as (C) Control. Morphological changes associated with EMT are shown in phase-contrast images. The presence of spindle-shaped cells, increased intracellular separation and pseudopodia were noted in leptin-treated cells but not in HNK-treated cells. B. MCF7 cells were treated as in A and total lysates were immunoblotted for Occludin, Snail and Zeb2 expression levels. Actin was used as control. C. MCF7 cells were treated as in A, total RNA was isolated and expression levels of epithelial and mesenchymal marker genes was analyzed. Actin was used as control. D. Breast cancer cells were treated as in A, and subjected to immunofluorescence analysis (1000X magnification) of Zeb1. Bar-graphs show the fold-change in number of cells expressing nuclear Zeb. *p < 0.001, compared with untreated controls. #p < 0.001, compared with leptin-alone treatment. Leptin-induced nuclear translocation of Zeb1 was abrogated by HNK treatment. E. Breast cancer cells were treated as in A, and subjected to immunofluorescence analysis (200X magnification) of E-cadherin, and Occludin. Bar-graphs show the fold-change in number of cells expressing Occludin and E-cadherin. *p < 0.05, compared with untreated controls. #p < 0.01, compared with leptin-alone treatment. F. MDA-MB-231 cells derived tumors were developed in nude mice and treated with leptin and/or HNK (n = 6–8/treatment group). At the end of five weeks of treatment, tumors were collected. Total RNA was isolated from tumor samples and subjected to RT-PCR analysis for the expression of mesenchymal markers and transcription factors. G. Breast cancer cells were treated as in A and subjected to scratch-migration assay.
