FIGURE 1.
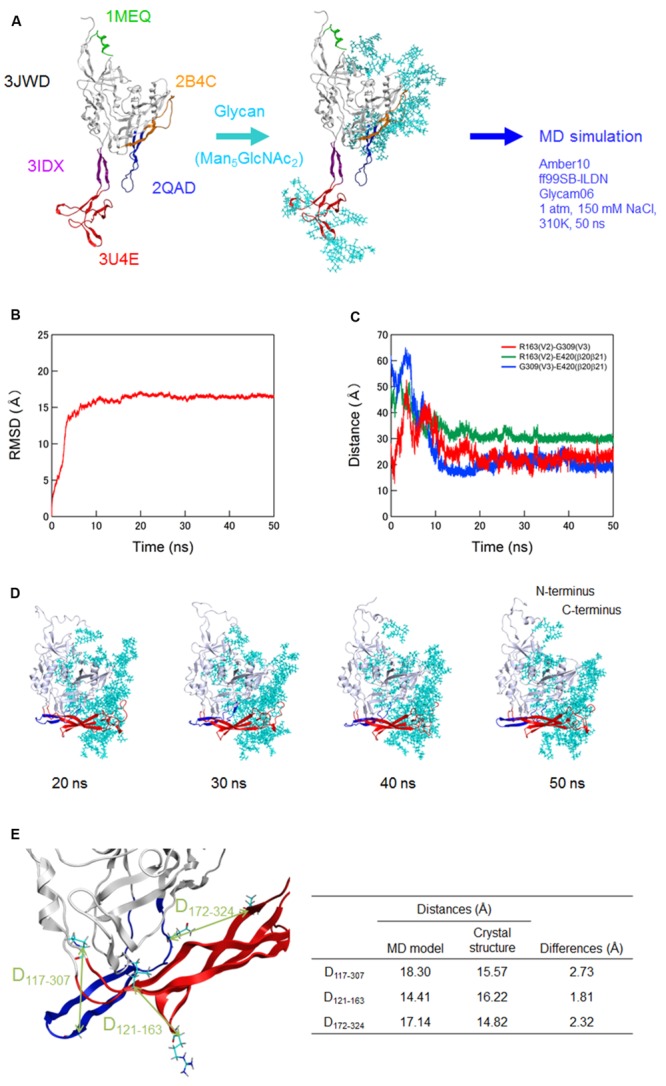
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of a full-length, glycosylated HIV-1JRFL gp120 monomer. (A) Schematic representation of molecular modeling and MD simulation. Molecular model for a full-length, glycosylated gp120 monomer of HIV-1 R5-tropic virus JRFL in a CD4-free state was constructed by assembling of HIV-1 gp120 parts and homology modeling. PDB codes of the structures used for modeling are indicated on the left. Thermodynamically and physically refined model was subjected to MD simulation using the PMEMD module in the AMBER 10 program package as described for simulations of HIV-1/SIV gp120 outer domains (Naganawa et al., 2008; Yokoyama et al., 2012; Kuwata et al., 2013; Yuan et al., 2013). (B) Time course of RMSD between the initial model and models at given times of MD simulation. RMSD values were calculated with trajectories at every 2 fs of MD simulation using the ptraj module in Amber 10. (C) Time course of distances between residues in V2 and V3 (red line), residues in V2 and β20-β21 (green line), and residues in V3 and β20-β21 (blue line) in gp120. (D) Structures of a full-length, glycosylated gp120 monomer at 20, 30, 40, and 50 ns of MD simulations. V1/V2 and V3 regions are highlighted by red and blue colors, respectively. (E) Distances between the variable loops and core. The distances between the Cα of P117 at core neighboring V1 base and Cα of G307 at the tip of V3 loop (D117-307), Cα of L121 at core neighboring V1 base and the Cα of R163 at V2 loop (D121-163), and Cα of L172 at V2 loop and the Cα of Q324 at V3 base (D172-324) were calculated with the gp120 model at 50 ns simulation and x-ray crystal structure (4TVP) to quantitatively compare relative 3-D locations of the V1/V2 and V3 loops on the core. Amino acid numbers are based on those of the JRFL Env protein (GenBank accession no. U63632).
