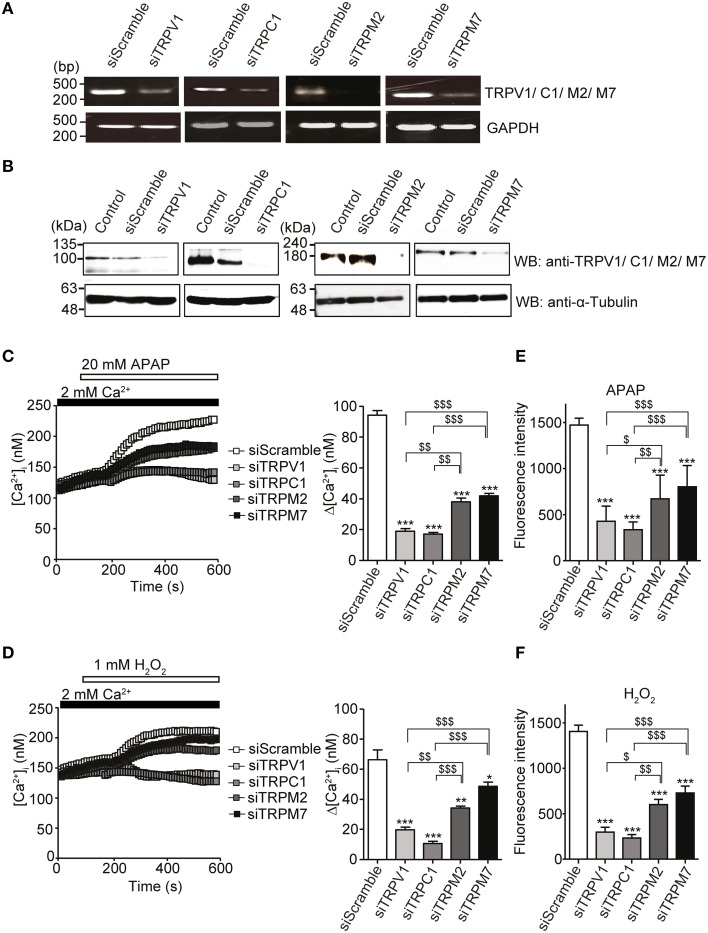
Figure 5.
Inhibition of APAP- or H2O2-induced Ca2+ responses and ROS production by siRNA-mediated knockdown of either TRPV1, TRPC1, TRPM2, or TRPM7 channel in HepG2 cells. (A) Effects of specific siRNA (siTRP) on channels of TRPV1, TRPC1, TRPM2, and TRPM7 mRNA levels detected by RT-PCR. GAPDH is used as a positive control. (B) Effects of siTRPV1, siTRPC1, siTRPM2, and siTRPM7 on levels of corresponding proteins detected by western blot. An anti-α-tubulin is used as a loading control. (C,D) [Ca2+]i changes induced by 20 mM APAP (C) or 1 mM H2O2 (D) in cells treated with siTRPM2, siTRPM7, siTRPV1, siTRPC1, or siScramble. Average time courses (left) and Δ[Ca2+]i (right) (n = 50–125). (E,F) Inhibitory effects of siTRPM2, siTRPM7, siTRPV1, siTRPC1, or siScramble on ROS produced by 20 mM APAP (E) or 1 mM H2O2 for 3 h (F). Data points are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared to siScramble. $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01, and $$$P < 0.001 compared to siTRPV1 or siTRPC1. All data of [Ca2+]i measurements were analyzed by Student's t-test, while those of ROS measurements were analyzed by ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc.