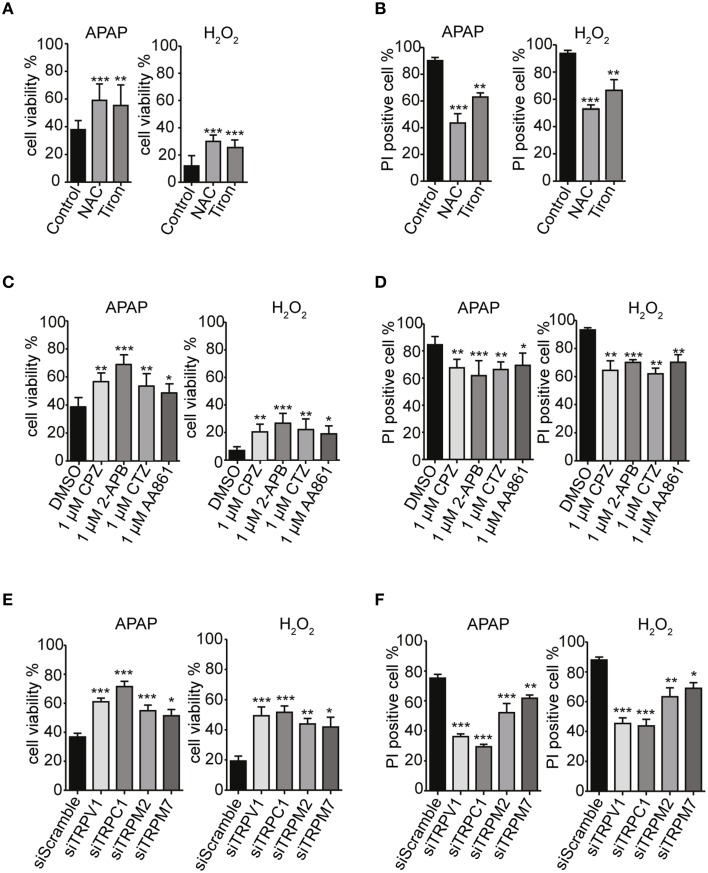
Figure 7.
TRPV1, TRPC1, TRPM2, and TRPM7 confer susceptibility to APAP-induced cell death via ROS in HepG2 cells. (A,B) ROS scavengers, NAC and tiron (1 mM), suppressed APAP- or H2O2-induced losses of cell viability (A) and increases of cell death (B) in HepG2 cells. (C,D) Selective TRP channels blockers, 1 μM of either CPZ, 2-APB, CTZ, or AA861 suppressed APAP- or H2O2-induced losses of cell viability (C) and increases of cell death (D) in HepG2 cells. (E,F) siRNA-mediated knockdown of TRPV1, TRPC1, TRPM2, and TRPM7 suppressed APAP- or H2O2-induced losses of cell viability (E) and increases of cell death (F) in HepG2 cells. Inhibitors are applied for 3 h before and during APAP or H2O2 stimulation. Data points are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared to the DMSO, siScramble or control. All data were analyzed by ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc.