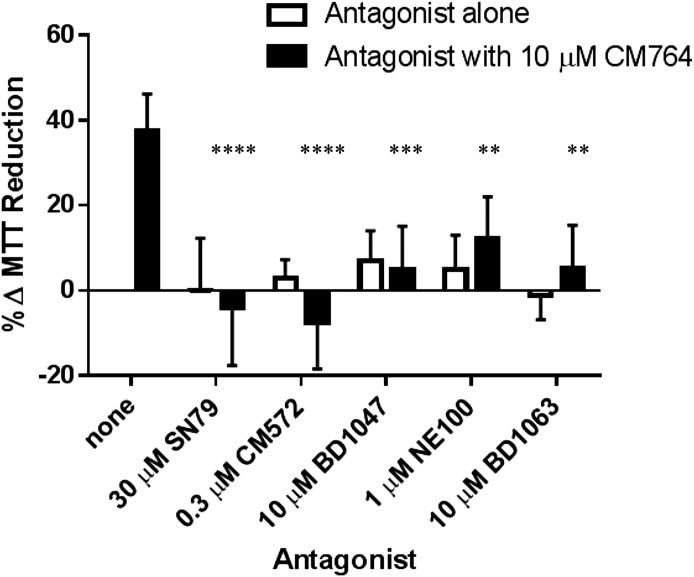
Fig. 5.
Effect of sigma-2 receptor antagonists on CM764-induced MTT reduction in SK-N-SH neuroblastoma. Cells were exposed to 10 μM CM764 alone, the indicated antagonist alone, or to the combination of 10 μM CM764 and antagonist for 24 hours. MTT reduction was measured as described in Materials and Methods. No antagonist alone produced a significant effect on MTT reduction compared with an untreated control. All antagonists were able to significantly attenuate the stimulative effect of CM764 on MTT reduction (one-way analysis of variance F = 13.73). CM572 and SN79, the most highly sigma-2 selective antagonists investigated, were both able to fully attenuate CM764-induced increase in MTT reduction (Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons compared with an untreated control, ****P < 0.0001). The other sigma-2 antagonists, although more selective for sigma-1 receptors, were also able to significantly attenuate CM764-induced MTT reduction. BD1047: ***P < 0.001; NE100: **P < 0.01; BD1063: **P < 0.01]. The data support the notion that the effect is sigma-2 receptor mediated. Results are presented as an average increase in MTT reduction compared with an untreated control for at least three independent experiments, with each experiment performed with five replicates per condition.