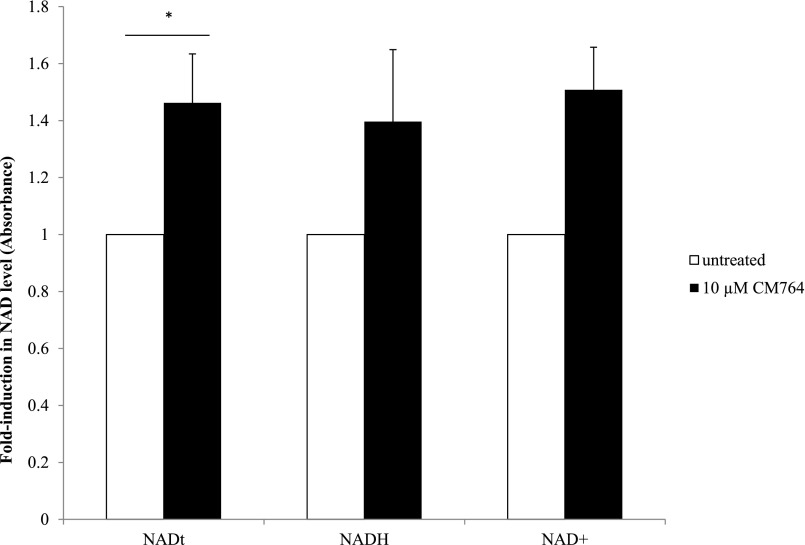
Fig. 7.
Changes in NADH/NAD+ in response to CM764 exposure. Cells were exposed to 10 μM CM764 for 24 hours prior to NADH/NAD+ assay, carried out as described in Materials and Methods. Treatment with CM764 induced a statistically significant, yet not robust ∼1.4-fold increase in total NAD (NADH + NAD+) compared with an untreated control [Student’s t test, P < 0.05 (P = 0.043)]. NADH and NAD+ levels each showed a similar trend to total NAD, but did not reach statistical significance. Results are presented as an average fold increase in absorbance in treated wells compared with an untreated control for three independent experiments ± S.D., with each experiment being performed in triplicate.