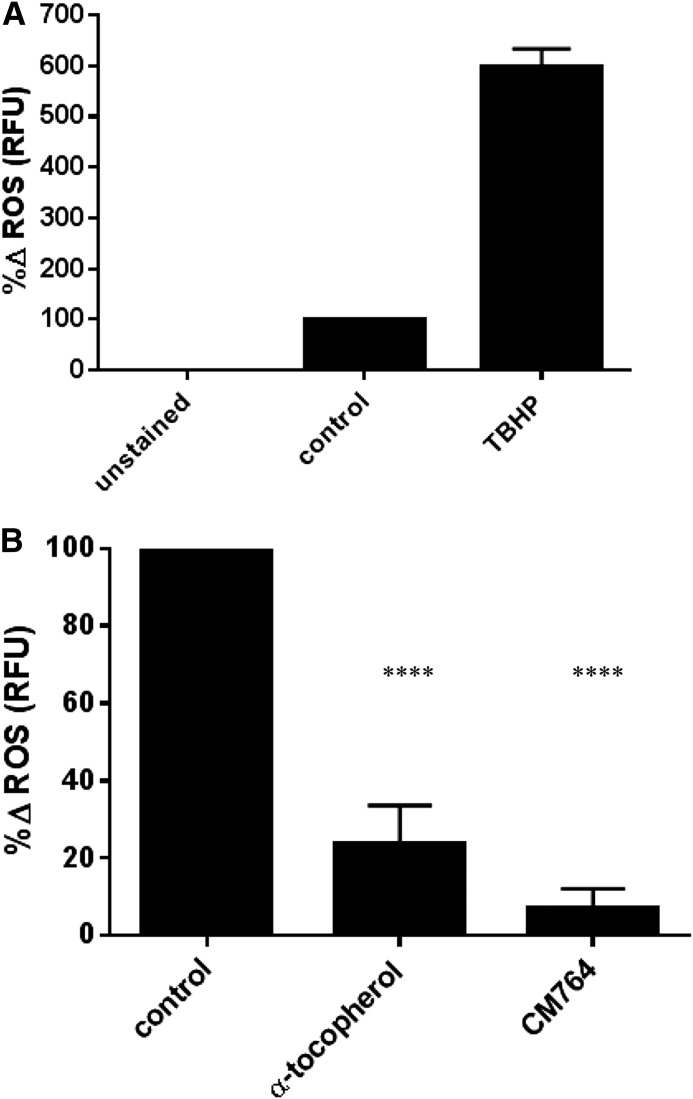
Fig. 9.
Effect of CM764 on ROS levels in SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells. Cells were stained with DCFDA prior to treatment with 10 μM CM764 for 4 hours, followed by fluorescence measurement as described in Materials and Methods. The effectiveness of the assay, showing the effect of 500 μM tert-butyl hydrogen peroxide (TBHP) as a positive control for the production of ROS is demonstrated in (A). The results of treatment with the antioxidant α-tocopherol (vitamin E, 200 μg/ml) and treatment with 10 μM CM764 are shown in (B). Treatment of SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells with CM764 resulted in a marked decrease in ROS that was more effective than that of α-tocopherol (95% and 76%, respectively). Results were highly significant (one-way analysis of variance F = 238.4, Dunnett’s test for multiple comparisons compared with the untreated control; ****P < 0.0001 for α-tocopherol, ****P < 0.0001 for CM764). Results are presented as an average of the percent change in ROS levels achieved ± S.D. compared with an untreated control normalized to 100% for three independent experiments, each experiment having four replicates per condition.