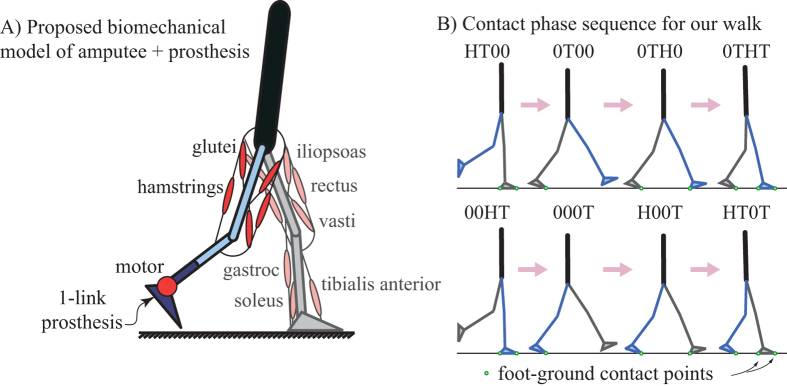
Figure 1.
(A) A sagittal-plane rigid-body model, with six human body segments and one prosthesis segment, connected via revolute joints. The leg without amputation uses eight muscles (iliopsoas, gluteus, hamstring, rectus femorus, vastus lateralis, gastrocnemius, soleus, and tibialis anterior); the leg with amputation uses identical muscles but removing and replacing all muscles crossing the ankle with a single prosthesis torque motor at the ankle. (B) Contact phase sequence for a natural walking motion. The four letter code refers to the points contacting the ground; heel and toe of the biological and prosthetic foot with 0 signifying no contact.