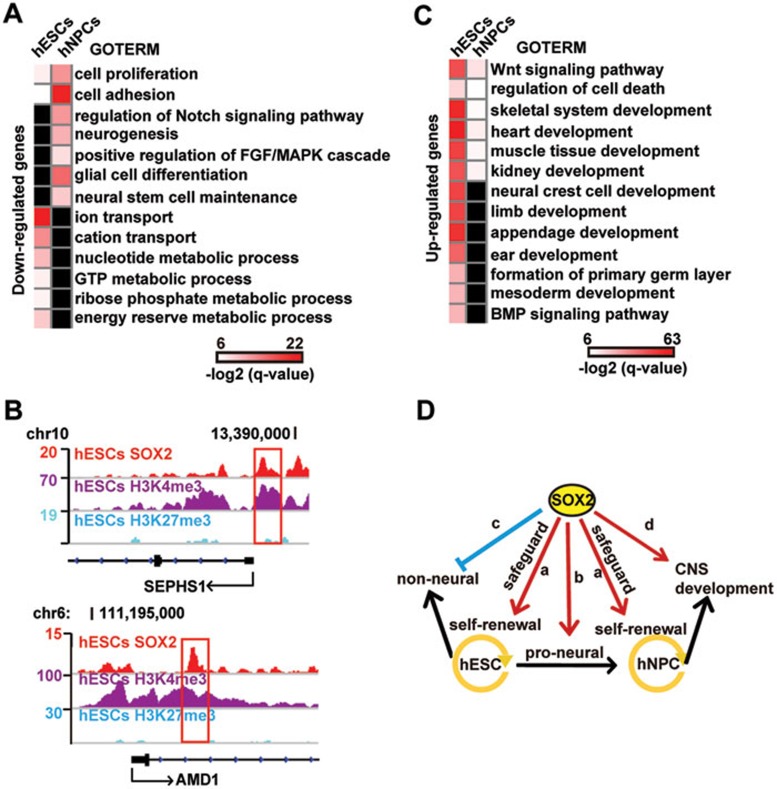
Figure 3.
SOX2 ensures self-renewal and differentiation potential of hESCs and hNPCs through dynamic control of distinct transcriptional programs. (A) GO analyses of common and specific features of downregulated genes in hESCs and hNPCs. si2/3-1 and si2/3-2 are two sets of oligos used for SOX2/3 KD in hESCs; si2-1 and si2-2 are for SOX2 KD in hNPCs. Cells were collected on day 3 of KD for RNA-seq. Analysis was done using genes altered by both sets of oligos in each cell type. Benjamini-Hochberg method is used to adjust the P-values in order to account for multiple testing. Enrichment levels of selected GO terms are marked by −log2(q-value). Missing values are marked in black. (B) Integrative Genomics Viewer screenshots showing SOX2 peaks on the active promoters of SEPHS1 and AMD1. (C) GO analyses of common and specific features of upregulated genes in hESCs and hNPCs. Benjamini-Hochberg method is applied to adjust the P-values in order to account for multiple testing. Enrichment levels of selected GO terms are marked by −log2(q-value). Missing values are marked in black. (D) An illustrative diagram showing SOX2-regulated cell type- and stage-dependent transcriptional programs: a, common in both cell types to safeguard the stem cell identity; b, proneural differentiation in hESCs; c, inhibition of non-neural lineages in hESCs; d, regulation of neurogenesis in hNPCs.