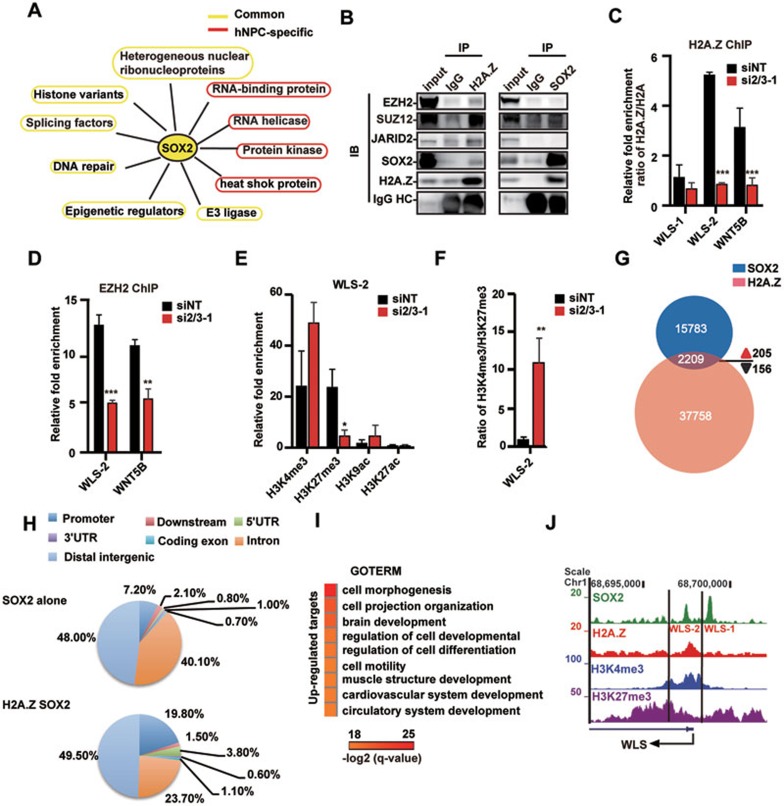
Figure 7.
SOX2 interacts with H2A.Z to recruit PRC2 and poise developmental genes in hESCs. (A) SOX2 protein partners in hESCs and hNPCs are classified into 10 categories. Protein partners common in the two cell types or specific to one of the cell types are shown. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation results of the interaction between H2A.Z, SOX2 and PRC2 components (EZH2, JARID2 and SUZ12) in hESCs. IB, immunoblotting; HC, immunoglobulin heavy chain. (C, D) ChIP-qPCR for H2A.Z (C) and EZH2 (D) binding at promoters of WLS and WNT5B in NT and SOX2/3 KD H9 hESCs. (E, F) ChIP-qPCR analysis of histone modification enrichments (E) and the ratio of H3K4me3/H3K27me3 at the WLS-2 site (F) in NT and SOX2/3 KD hESCs. (G) A Venn diagram showing the overlap between target regions of SOX2 and H2A.Z in hESCs. Numbers of indicated peaks and altered genes upon SOX2/3 KD are shown. (H) The genomic distribution of SOX2 alone sites and SOX2-H2A.Z co-localized sites. (I) GO analysis of common targets of SOX2 and H2A.Z that are upregulated upon SOX2/3 KD in hESCs. Benjamini-Hochberg method is applied to adjust the P-values in order to account for multiple testing. Enrichment levels of selected GO terms are marked by −log2(q-value). (J) Integrative Genomics Viewer screenshots showing enrichments of H3K4me3, H3K27me3, H2A.Z and SOX2 on the promoter of WLS.