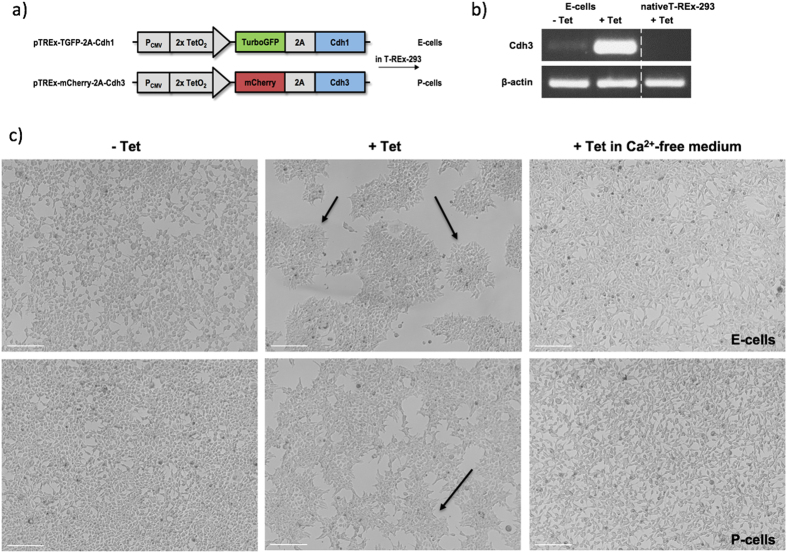
Figure 1. Introduction to the tools used to construct a phase-separation-based patterning system in living cells.
(a) Cdh1 and Cdh3 constructs were used to transfect T-REx-293 cells to produce E-cells (characterized in a previous publication:9) and P-cells. (b) Levels of murine Cdh3 transcripts in P-cells induced (‘ + Tet’) or uninduced (‘−Tet’) with tetracycline for 48 h and in T-Rex-293 wild-type cells in the presence of tetracycline, confirming inducibility. The band showing β-actin, a ‘housekeeping’ protein that should be unaffected by tetracycline, is a control to demonstrate equal loading of the RT-PCR reaction and gel. A similar analysis for the Cdh1 transcript has been presented in9. (c) Comparison of E-cell and P-cell cell morphology after 48 h of culture with or without tetracycline. In the absence of tetracycline, cells were scattered with no obvious adhesive islands. Following induction, adhesive islands formed (arrows), being more smooth-edged in E-cells than in P-cells. The adhesion clusters observed in the presence of tetracycline were disrupted in calcium-free medium, as would be expected for a cadherin-dependent mechanism. Scale bars: 200 μm.