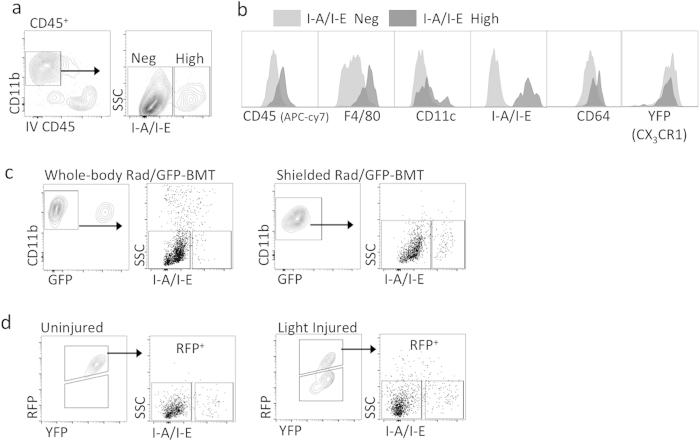
Figure 6. Analysis of extravascular I-A/I-Ehi myeloid cells in normal retina.
(a) Identification of I-A/I-Ehi myeloid cells in the retina. Cells were pre-gated on live CD45+ singlets. (b) I-A/I-Ehi cells in the normal retina are putative MFs, as indicated by positive CD64 and F4/80 expression. Data is representative of two independent experiments; each experiment has n = 4 individual samples. (c) Evaluation of I-A/I-Ehi putative MFs, regarding long-lived and radio-resistant status. Mice were subjected to whole-body or shielded Rad/GFP-BMT then retinas were harvested 3 months later. I-A/I-Ehi putative MFs were evident following shielded, but not whole-body, Rad/GFP-BMT. Cells were pre-gated on live CD45+ singlets. Data is representative of 2 independent experiments; each plot is representative of 2 to 4 individual samples. (d) Fate mapping in CX3CR1YFP−CreER/wt:R26RFP mice to further evaluate possible long-lived status of I-A/I-Ehi putative MFs. Mice were tamoxifen pulsed. Then after 3 months, mice were subjected to light challenge (or not) and retinas were harvested 5 days later for flow cytometry analyses. Long-lived RFP+ cells were analyzed for the presence/absence of I-A/I-Ehi putative MFs. Cells were pre-gated on live CD45+ CD11b+ singlets. Data is representative of two independent experiments; each experiment contained data from individual samples, uninjured n = 2 and injured n = 5.