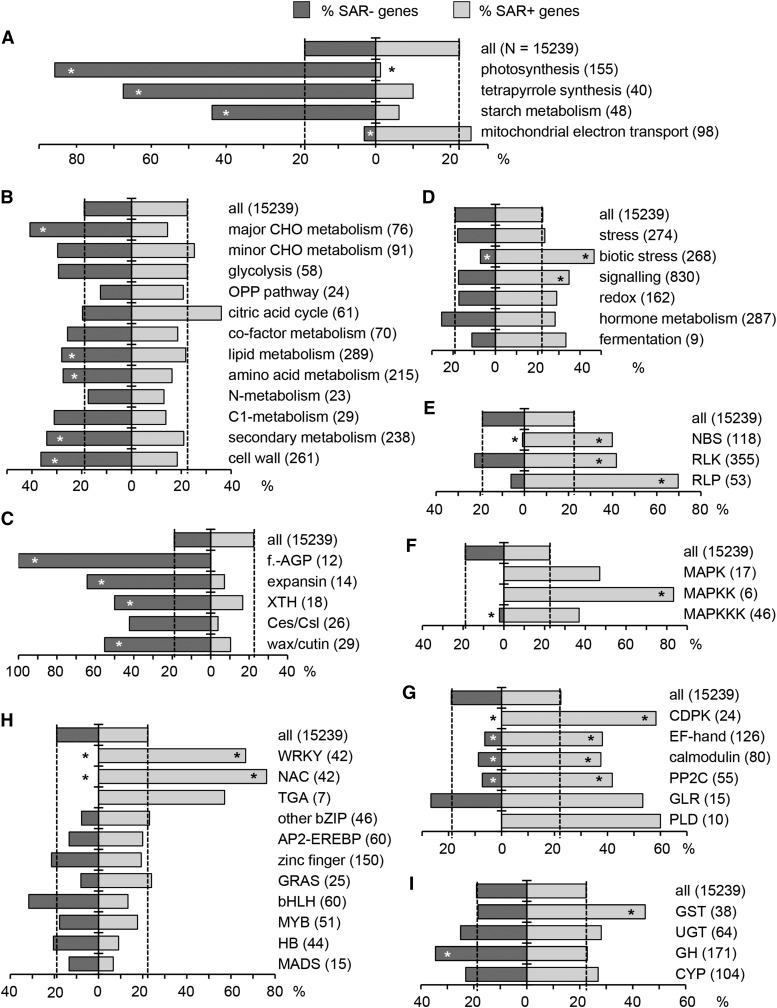
Figure 4.
Percentage of SAR+ and SAR− Genes in Defined Gene Groups Representing MapMan Metabolic Pathways, Functional Categories, or Arabidopsis Gene Families (http://www.arabidopsis.org).
Dashed vertical lines illustrate the percentage of SAR+ and SAR− genes in the whole, RNA-seq-covered transcriptome (28,496 genes) after threshold cutoff (15,239 genes). The number of genes in each category is given in parentheses. Asterisks on the bars indicate significant enrichment or depletion of gene categories in SAR+ (right) and SAR− (left) genes (Fisher’s exact test, P < 0.01).
(A), (B), and (D) MapMan metabolic pathways and functional categories.
(C) Gene families involved in cell wall remodeling and wax/cutin biosynthesis. f.-AGP, fasciclin-like arabinogalactan proteins; XTH, xyloglucan endotrans-glucosylase/hydrolases; Ces/Csl, cellulose synthase/cellulose synthase-like.
(E) Gene families involved in the perception of microbial structures and early defense signal transduction. NBS, nucleotide binding site-containing resistance proteins; RLP, receptor-like proteins.
(F) MAPK cascade members. MAPKK, MAPK kinase; MAPKKK, MAPK kinase kinase.
(G) Other gene categories involved in defense signaling. CDPK, calcium-dependent protein kinases; EF-hand, EF-hand-containing proteins; calmodulin, calmodulin binding proteins; GLR, glutamate receptor-like family; PLD, phospholipase D family.
(H) Main transcription factor families. WRKY, WRKY domain family; NAC, NAM-ATAF1,2-CUC2 transcription factors; TGA, TGACG motif binding factor; bZIP, basic leucine zipper; AP2-EREBP, APETALA2 and ethylene-responsive element binding proteins; zinc finger, zinc finger superfamily; GRAS, GRAS family; bHLH, basic helix-loop-helix; MYB, MYB family; HB, homeobox-leucine zipper; MADS, MADS box.
(I) Genes for different enzyme classes. GST, glutathione S-transferases; UGT, UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases; GH, glycosyl hydrolases; CYP, cytochrome P450 superfamily.