Fig. 4.
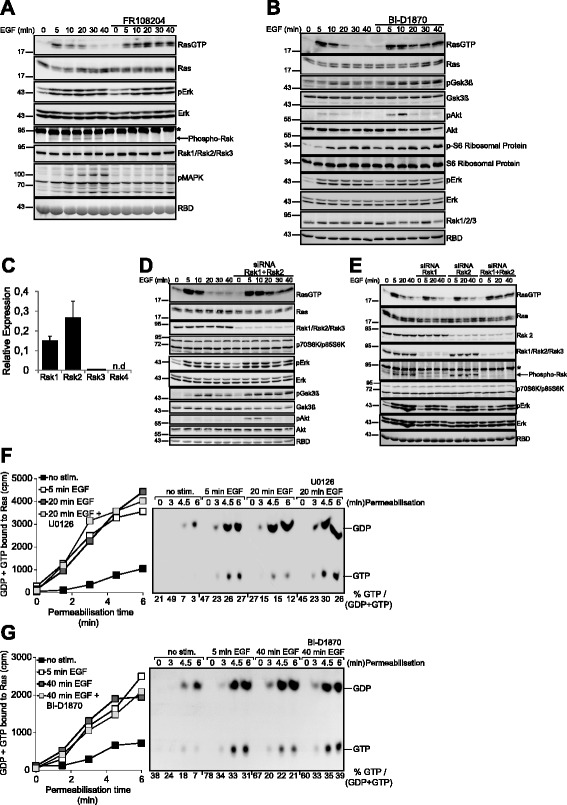
Rsk1 and Rsk2 mediate the feedback deactivation of Ras. a HeLa cells treated or not with the Erk inhibitor FR108204 were challenged with EGF for the indicated periods of time and subjected to a Ras-GTP pulldown assay. The phosphorylation/activation state of the indicated proteins was determined using phophosite-specific antibodies. Phospho-MAPK Substrates (PXS*P or S*PXR/K): Ab recognizing the phosphorylated Erk consensus motif. Asterisk denotes an unspecific band. b Same experiment in cells pre-treated with the pan-Rsk inhibitor BI-D1870. The activation status of Erk was monitored using phospho-site specific antibodies against Erk. Acute inhibition of Rsk with BI-D1870 did not affect Rsk protein stability as illustrated by the immunodetection of total Rsk1/Rsk2/Rsk3. c Real-time PCR analysis of Rsk isoform expression in HeLa cells. d Rsk1 and Rsk2 were simultaneously silenced via siRNA in HeLa cells followed by stimulation with EGF and biochemical analysis of Ras activation. e Biochemical determination of Ras-GTP levels and Erk activity in HeLa cells previously subjected to single or combined siRNA-mediated knockdown of Rsk1 and Rsk2. Immunodetection of p70S6K/p85S6K was performed as a control of specificity of the siRNA-mediated knockdown of Rsk1/2. Asterisk denotes an unspecific band. f Feedback deactivation of Ras is mediated via GAP up-regulation. HeLa cells were pretreated with U0126 where indicated, challenged with 10 ng/ml EGF and subjected to analysis of Ras nucleotide exchange. g Same experiment as in (a) performed in cells treated with the pan-Rsk inhibitor BI-D1870
