Fig. 3. Oxygen consumption and rescue of bacterial growth and oxygen consumption by menaquinone (Vitamin K2).
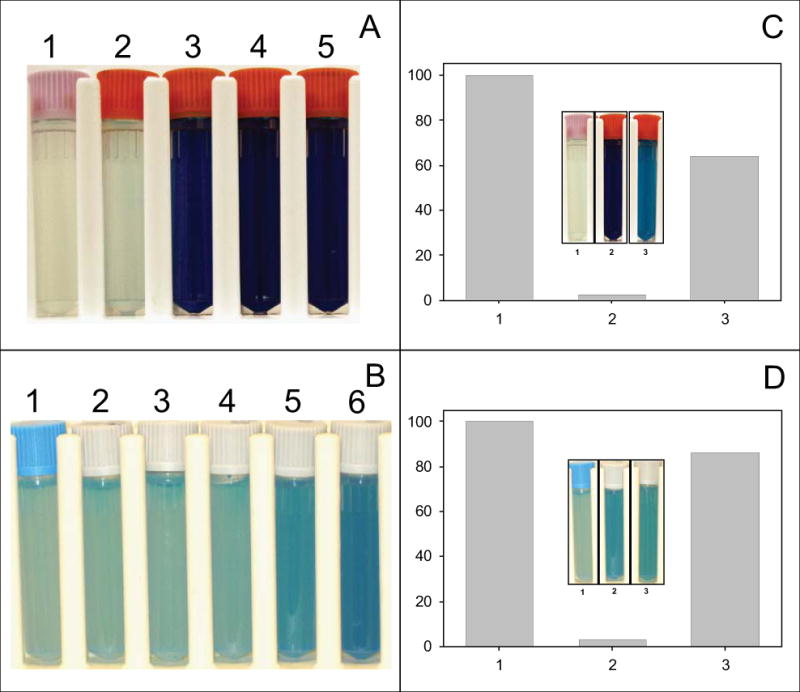
Panel A – M. smegmatis cultures, containing 0.01% methylene blue, treated with Ro 48-8071 at 0, 10, 25, 50 or 100 ug/ml, tubes 1–5 respectively. Cultures were incubated at 37° C for 2 h. Panel B – M. tuberculosis cultures, containing 0.03% methylene blue, treated with Ro 48-8071 at 0, 5, 10, 25, 50 or 100 ug/ml, tubes 1–6 respectively. Cultures were incubated at 37° C for 8 h. Panel C – M. smegmatis was cultured in the presence of 0 μM Ro 48-8071 (lane 1), 20 μM Ro 48-8071, or 20 μM plus 400 μM Vitamin K2 (lane 3) for 24 h. Growth rates were monitored by measuring OD @ 600nm. Inset – M. smegmatis cultures, containing 0.01% methylene blue, were treated with 0 μg/ml Ro48-8071 (tube 1), 50 μg/ml Ro48-8071 (tube 2) or 50 μg/ml Ro48-8071 plus 400 μM Vitamin K2 (tube 3) and incubated at 37° C for 2 h. Panel D – M. tuberculosis was cultured in the presence of 0 μM Ro 48-8071 (lane 1), 20 μM Ro 48-8071, or 20 μM plus 400 μM Vitamin K2 (lane 3) for 12 days; growth rates were monitored by measuring OD @ 600nm. Inset – M. tuberculosis cultures, containing 0.03% methylene blue, were treated with 0 μg/ml Ro48-8071 (tube 1), 50 μg/ml Ro 48-8071 (tube 2) or 50 μg/ml Ro 48-8071 plus 400 μM Vitamin K2 (tube 3) and incubated at 37° C for 8 h. Culture medium was as indicated in Experimental Procedures.
