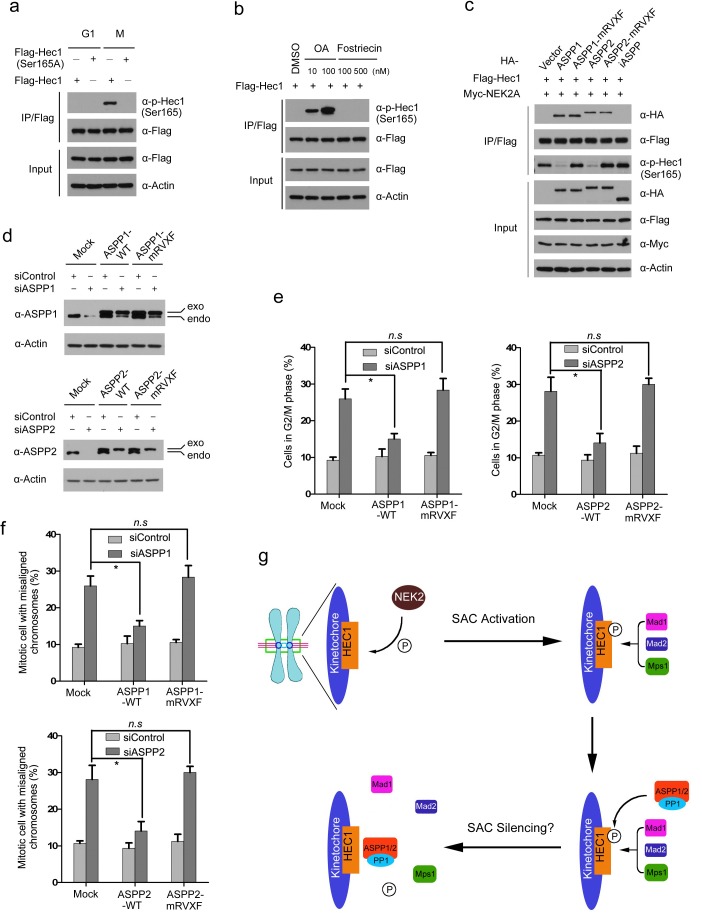
Figure 6. ASPP1/2-PP1 complexes dephosphorylate mitotic Hec1 at Ser165.
a. HeLa cells were transfected with Flag-Hec1 WT or S165A mutant. Cells were synchronized at the G1/S (double-thymidine block) or M phase (nocodazole). Cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation with the anti-Flag antibody and detected by WB analyses using the indicated antibodies. b. 293T cells were transfected with Flag-Hec1. After 24hr, the cells were treated with different doses of Okadaic acid (OA) or Fostriecin for another 12hr. Cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation with the anti-Flag antibody and detected by WB analyses using the indicated antibodies. c. ASPP1/2 antagonize NEK2A-mediated Hec1 Ser165 phosphorylation. 293T cells were co-transfected with indicated constructs. After 24 hr, cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation with the anti-Flag antibody and detected by WB analyses using the indicated antibodies. d. WB analyses of ASPP1/2 proteins following siRNA treatment in HeLa cells stably expressing a FH-ASPP1/2 (WT or mRVXF) constructs resistant to the siRNAs targeting endogenous ASPP1/2. (e., f.) Stable expression of siRNA-insensitive FH-ASPP1/2, but not the mRVXF mutants, in siRNA-treated HeLa cells rescued G2/M arrest (e) chromosome misalignment (f) caused by ASPP1/2 depletion. The cell-cycle distributions of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 48 hr were determined by flow cytometry. Error bars, SEM *p<0.01 from triplicates. n.s, not statistically significant. (f) Model.