Figure 5. HRAS mutants transform Ba/F3 cells which become sensitive to MEK and mTOR inhibition.
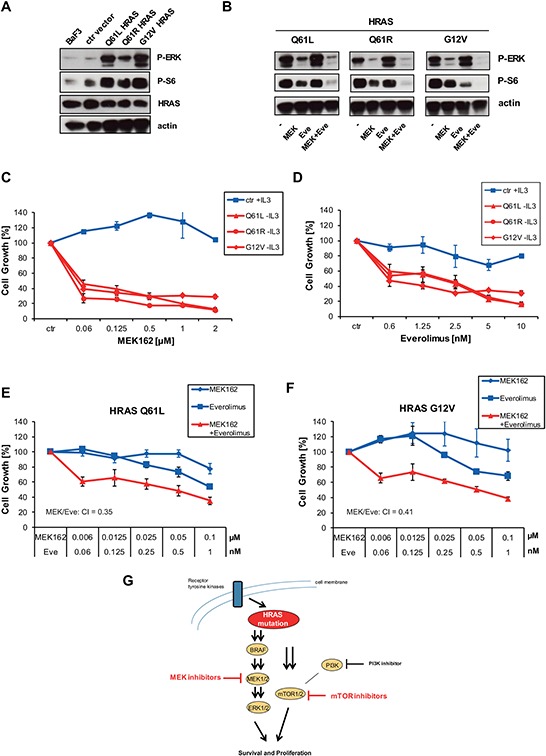
A. Ba/F3 cells or Ba/F3 cells transduced with empty vector were kept under 0,1 ng/ml IL-3. Ba/F3 cells transduced with HRAS Q61L, Q61R or G12V grew independent of IL-3 and were kept under puromycin selection with 1ug/ml. Cells were lysed and analysed by Western blot with indicated antibodies. B. Ba/F3 clones were kept under same conditions as described in A. Cells were treated with 250nM AZD6244, 5nM of Everolimus or combinations thereof as indicated for 1 hour. Then, cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blot. C. Ba/F3 clones were kept under same conditions as described in A. Ba/F3 cells transduced with empty vector or HRAS Q61L, Q61R or G12V were treated with increasing concentrations of MEK162. Then, cell growth was measured by Cell Titer Glo after 96 h. D. Same as in C., but Everolimus was used instead. E, F. HRAS Q61L or G12V expressing clones were left untreated or treated with indicated concentrations of Everolimus and MEK162 for 96 hours. Then, cell growth was measured by Cell Titer Glo. CIs are indicated. G. Schematic representation of mutant HRAS signaling pathways. Mutant HRAS can be blocked by inhibition of downstream MEK and mTOR but not by PI3K.
