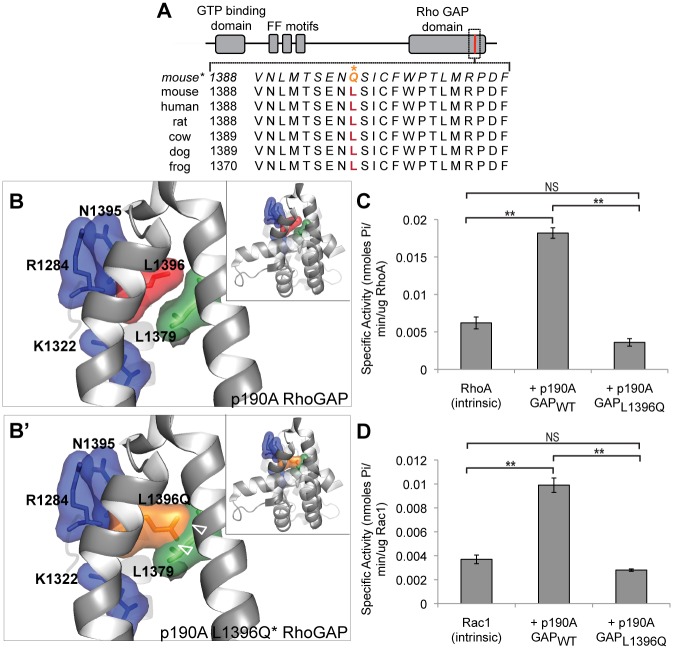
Fig 3. L1396Q substitution in the p190A GAP domain is a loss-of-function mutation.
(A) Protein sequence alignment around leucine 1396 (red) shows high conservation across species. The predicted L1396Q mutation (*) is indicated in orange. (B-B’) Structure of the human p190A GAP domain (PDB 3FK2) residues around L1396 [red], including RhoA-interacting residues R1284, K1322, and N1395 [blue] and nearby residue L1379 [green], reveals substantial steric clashes with the substituted glutamine [L1396Q, orange](open arrowhead). Insets show the full GAP domain structure. (C-D) In vitro Rho-family GTPase activity assays in the absence of recombinant p190A GAP domain (intrinsic), with the wild type (p190A GAPWT) or point mutant (p190A GAPL1396Q) domains reveal a loss of GAP activity of the mutant form for recombinant RhoA (panel C) and Rac1 (panel D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (one-way ANOVA)