Figure 1. The dimeric structure of hGal-7.
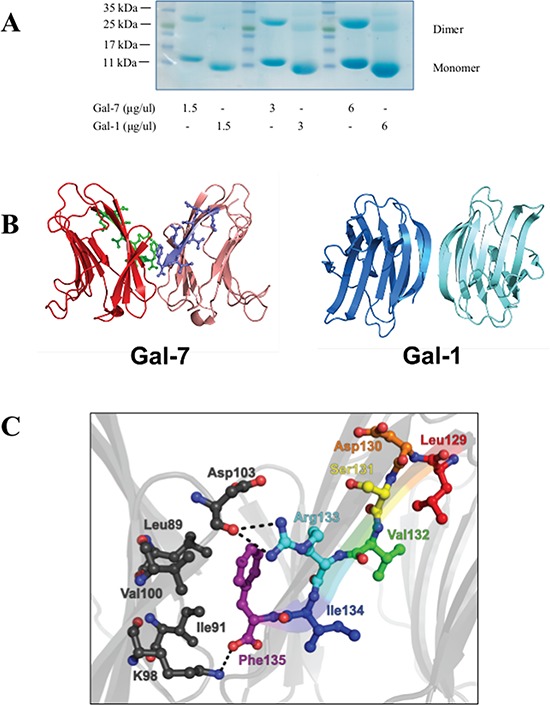
A. Dimer formation of recombinant hGal-7 and hGal-1 at increasing concentrations were compared by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in native conditions. B. Structural representation of the hGal-7 (PDB 1BKZ) and hGal-1 (PDB 3W58) dimers with residues 129–135 colored in green and magenta on the hGal-7 dimer interface. Dimer formation in hGal-7 proceeds through a “back-to-back” topology of the monomers while hGal-1 adopts a “side-by-side” structural arrangement, affording additional specificity for galectin inhibition. C. Molecular interactions implicated in the wild-type hGal-7 dimer interface between residues 129–135 of the first hGal-7 monomer (in various colors) and facing residues on the second hGal-7 monomer (in black) (PDB 1BKZ). Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions are identified as dashed lines. The side chain of Phe135 is also involved in a number of van der Waals interactions [29]. The structures were prepared with PyMOL.
