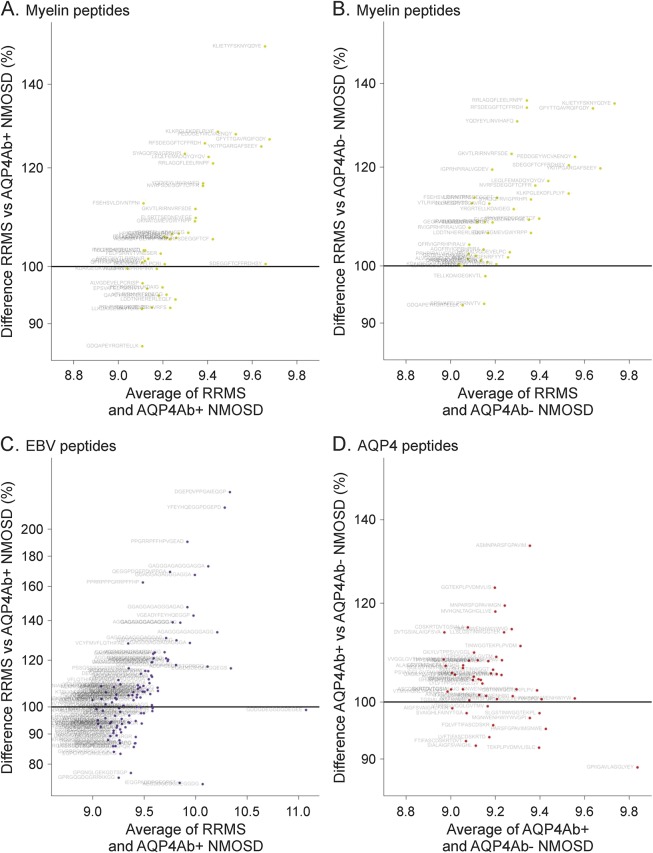
Figure 2. Elevated antibody reactivities against myelin and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) peptides in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) and higher anti–aquaporin-4 (AQP4) peptide reactivities in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders positive for AQP4−Abs (AQP4Ab+ NMOSD).
Comparison of selected peptide groups in different patient subsets shown with MA plots. (A) Myelin peptides RRMS vs AQP4Ab+ NMOSD. (B) Myelin peptides RRMS vs AQP4Ab− NMOSD. (C) EBV peptides RRMS vs AQP4Ab+ NMOSD. (D) AQP4 peptides AQP4Ab+ vs AQP4Ab− NMOSD. Each dot represents one peptide. The x-axis displays the average normalized signal to show the general level of peptide binding. The y-axis indicates the difference between the patient groups given as a percentage. Greater reactivities in the first mentioned group are found above the 100% horizontal line, and lower reactivities below this line. Patients with RRMS show higher antibody reactivities against myelin peptides and EBV-EBNA 1 peptides than do patients with NMOSD. Higher antibody reactivities against AQP4 peptides are evident in the AQP4Ab+ compared to the AQP4Ab− NMOSD group.