Fig 5. Effect of 5Hz rTMS over the SMA on Recovery from Fatigue.
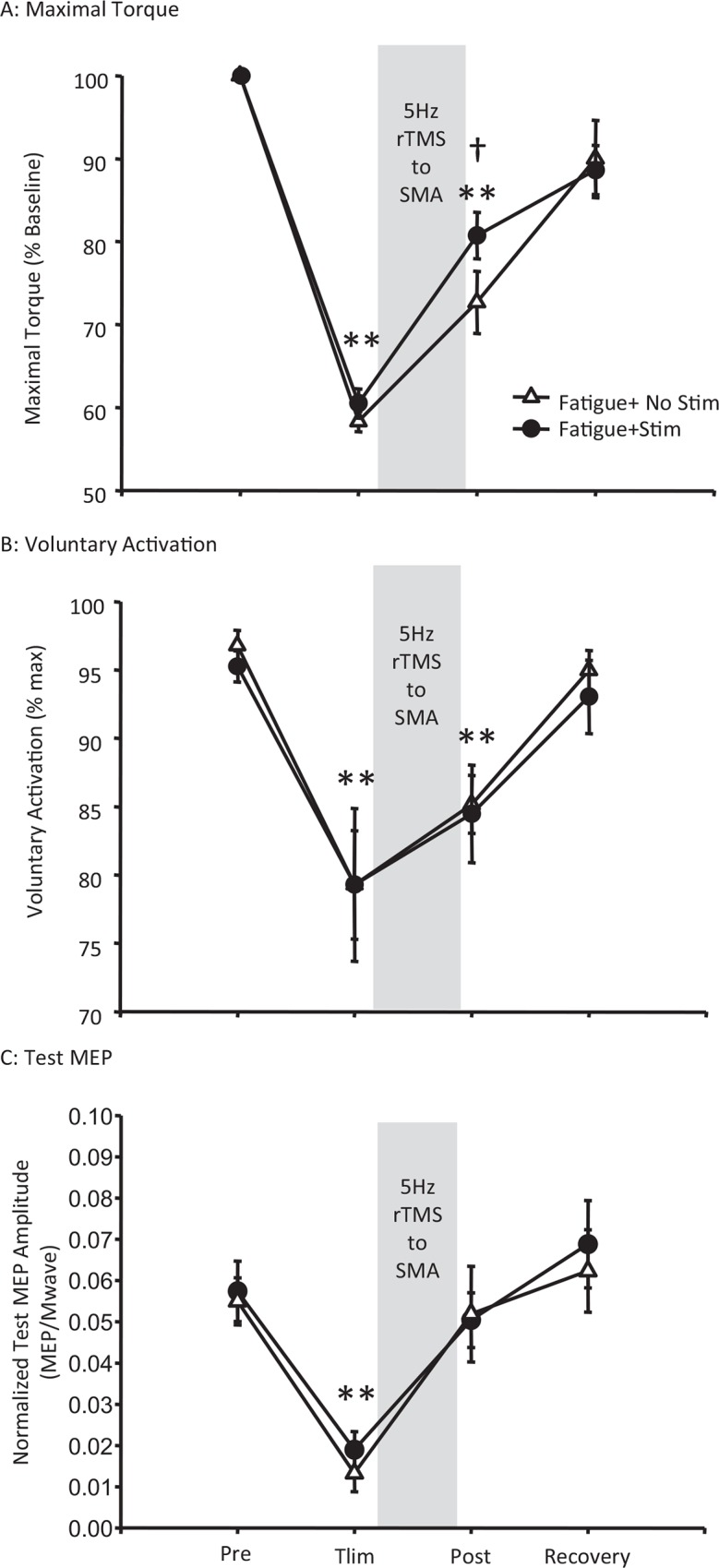
Maximal torque (A), maximal voluntary activation (B) and test MEP amplitude (C) were significantly reduced at task failure however rTMS to the supplementary motor area (SMA) increased the rate of recovery of maximal torque but not maximal voluntary activation or MEP amplitude. Data are presented as mean±S.E on a fatigue day where stimulation was applied to the supplementary motor area (circles) or no stimulation control day (triangles). ** indicate significant differences from baseline on both days. † indicate significant difference between days (Fishers LSD post hoc, p<0.05).
