Fig 4. Orientation-specific unique transcriptional regulation by invertible IVp-I/IVp-II.
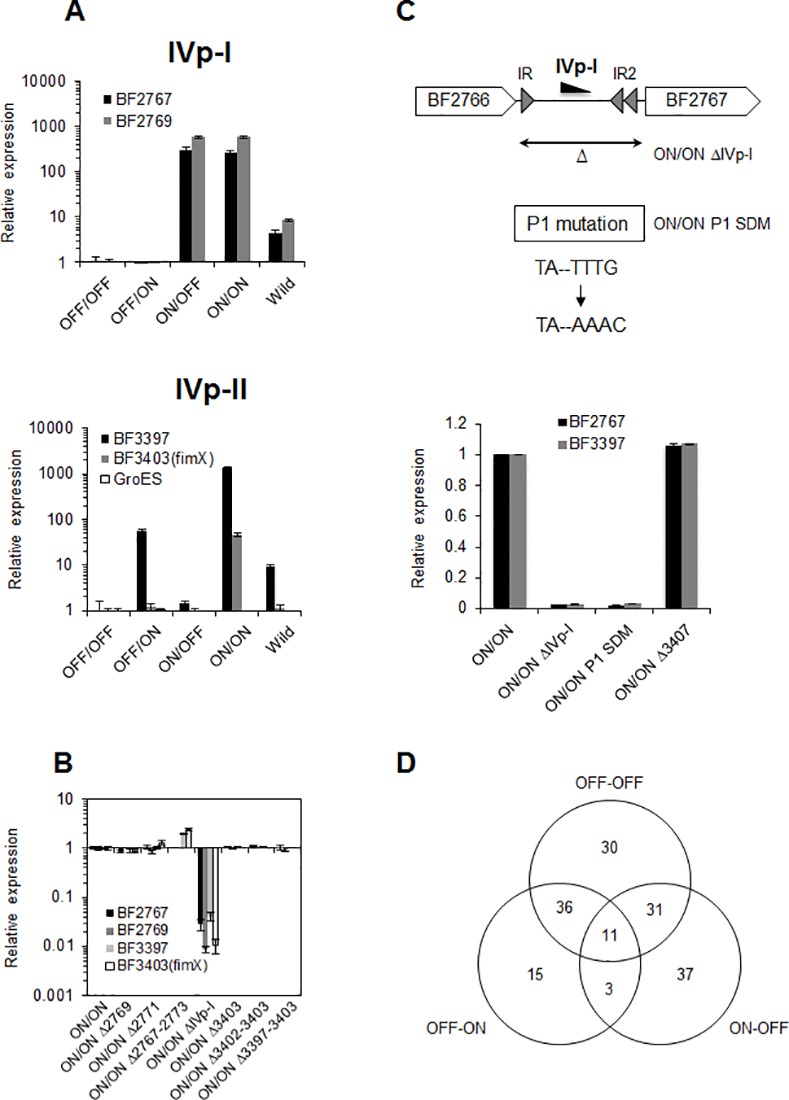
(A) The expression of EPS biosynthesis genes (represented as BF2767 and BF2769) and a gene cluster (represented as BF3397 and BF3403) were dependent on IVp-I and IVp-II, respectively. The transcriptional level of the IVp-II-regulated gene cluster in the hypervesiculating mutant (ON/ON) was increased 25- to 40-fold over that of the OFF/ON mutant. (B) IVp-I was required for the full expression of the gene cluster downstream of IVp-II. A variety of deletions were generated within the EPS production locus or at the IVp-II-regulated gene cluster in the hypervesiculating mutant (ON/ON). Only the deletion of the IVp-I-containing invertible DNA region affected the expression of IVp-II-regulated genes. (C) The effects of IVp-I activity and IVp-I-related IRs on IVp-II activity. IVp-I activity was attenuated after replacing the -7 sequence (TAnnTTTG is the Bacteroides consensus promoter sequence at -7) with an inactive form (TAnnAAC) by using site-directed mutagenesis. Two IRs were present between IVp-I and BF2767 in the ON/ON mutant obtained in this study. These IRs and the entire invertible fragment containing IVp-I were deleted to examine the role of these elements in IVp-II activity. (D) Venn diagram comparing differentially expressed genes in B. fragilis mutants with different IVp-I/IVp-II orientations. The number of differentially expressed genes (> 4-fold change) in each genotype was compared with the ON/ON genotype. The expression levels of 11 genes were specifically elevated in the ON/ON mutant (S2 Table).
