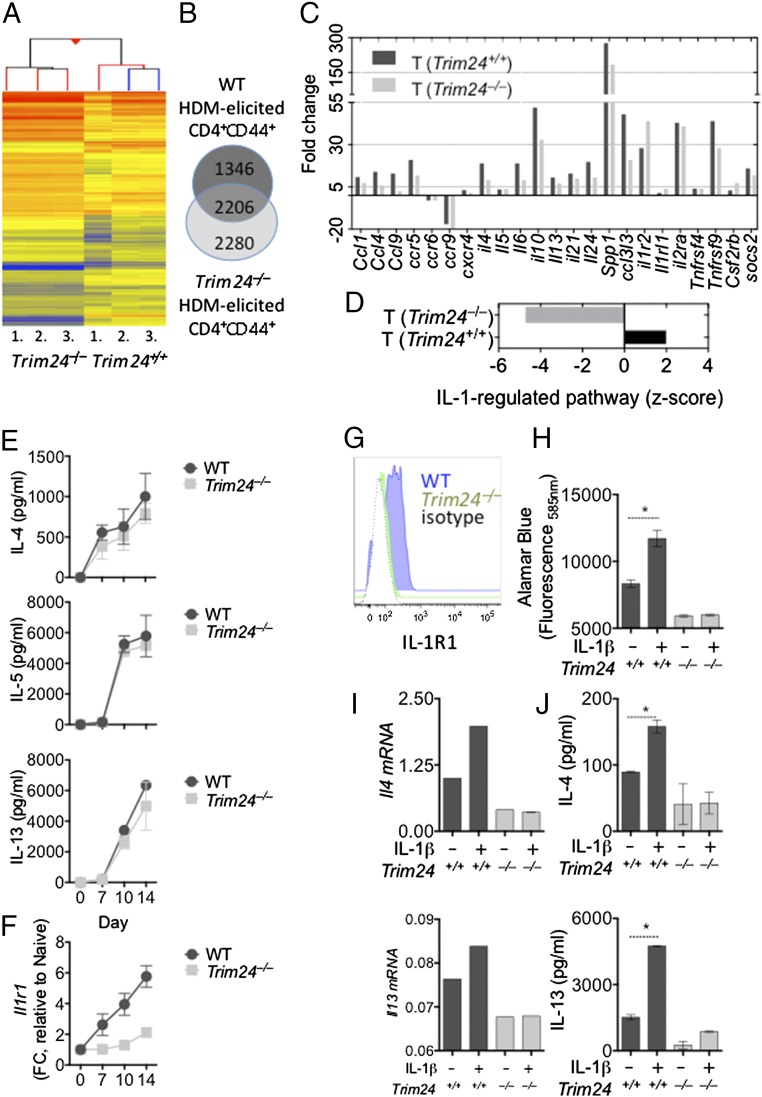
Fig. 3.
Transcriptional analysis of activated (CD44+) Trim24−/− T cells from the lungs of mice with identified airway allergy, reduced cytokine and chemokine expression, and reduced IL-1–regulated pathways. Chimeric mice with WT or Trim24−/− T cells were sensitized and challenged with HDM. Activated (CD4+CD44+) WT or Trim24−/− T cells were isolated from the lungs and FACS-purified for transcriptional analysis 1 d after the final airway challenge. *P ≤ 0.05. (A) Heat map of differentially expressed genes in WT and Trim24−/− T cells, relative to naive T cells. (B) Venn diagram showing common and unique genes regulated in WT and Trim24−/− T cells. (C) Noteworthy TH2 effector genes involved in airway allergy. (D) Z-score of the likelihood of activity for IL-1–regulated pathways in WT and Trim24−/− T cells. (E) Naive (CD4+CD44–CD62Lhi) WT and Trim24−/− T cells were FACS-purified and cultured under TH2 conditions for the indicated days. IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 were measured in supernatant. (F) WT and Trim24−/− T cells cultured under TH2 conditions were harvested at the indicated days. RNA was extracted, and Il1r1 expression was determined by qRT-PCR. (G) IL-1R1 expression on CD4+CD44hi WT and Trim24−/− TH2 cells at day 10. (H) Day 10 WT and Trim24−/− TH2 cells were washed, counted, and replated at 2 × 105 cells per well. Cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 in the presence or absence of IL-1β (10 ng/mL), as indicated. Cell viability/activity was determined by Alamar blue fluorescence. (I) Il4 and Il13 mRNA expression in day 10 WT and Trim24−/− TH2 cells. Expression is shown relative to Hprt. One of three representative experiments is shown. (J) IL-4 and IL-13 protein expression in supernatant from WT or Trim24−/− T cells. Expression is shown relative to Hprt. One of three representative experiments is shown.