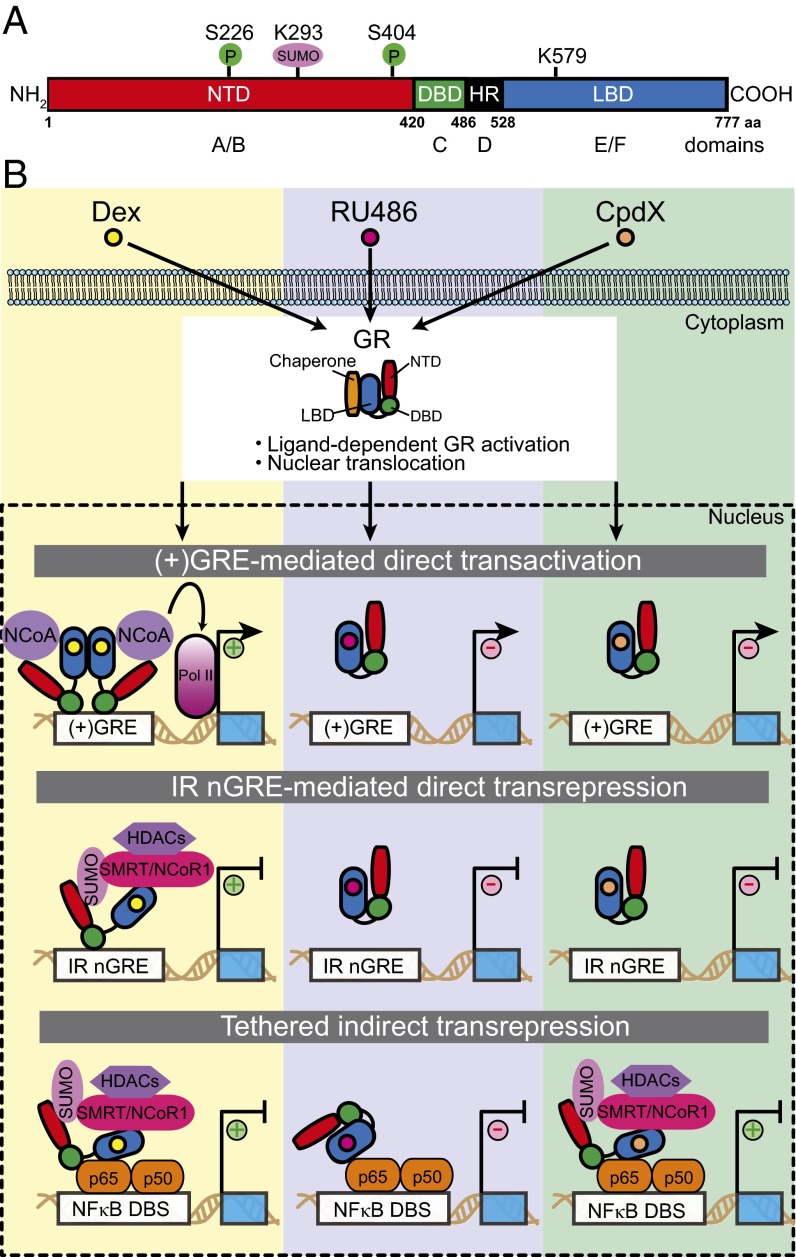
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration (A) of the structural domains within the human GR, indicating relevant phosphorylation (P), and SUMOylation sites, and (B) the three molecular mechanisms by which GR regulates expression of its target genes upon binding an agonist (e.g., dexamethasone, Dex), an antagonist (e.g., RU486), or a SEGRA (e.g., CpdX). “+” indicates stimulation of gene activation or repression, whereas “−” indicates no effect on stimulation or repression. DBD, DNA-binding domain; HR, hinge region; LBD, ligand-binding domain; NTD, N-terminal domain.