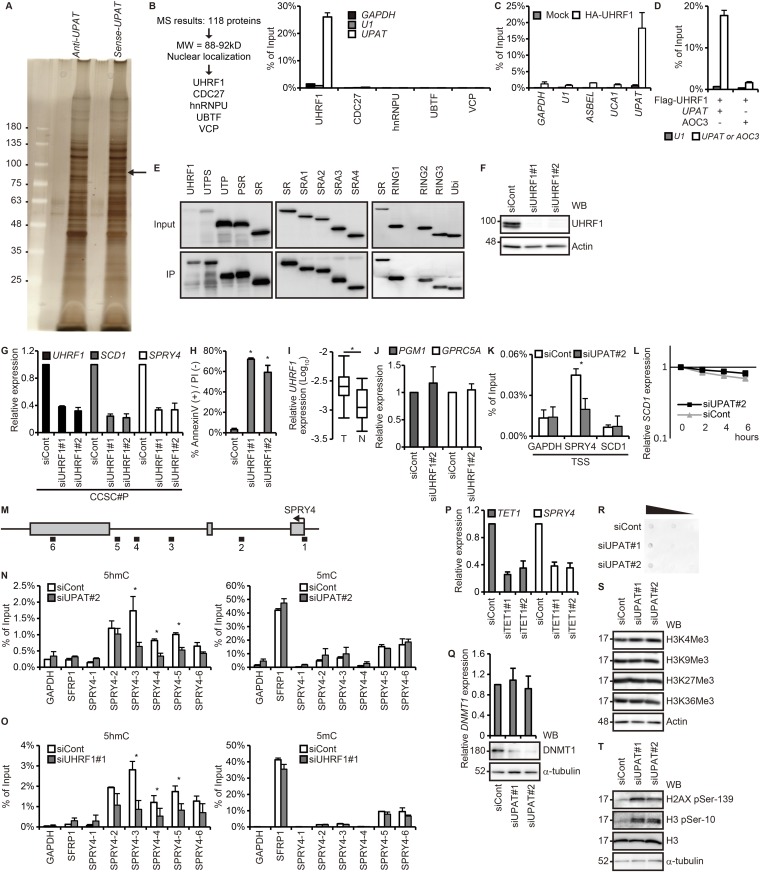
Fig. S3.
UPAT is associated with UHRF1 in colon cancer cells. (A) Nuclear extracts from HCT116 cells were incubated with biotinylated sense or antisense UPAT, and proteins precipitated with streptavidine beads were resolved by SDS/PAGE followed by silver staining. The band indicated by the arrowhead was excised and subjected to liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. (B, Left) The procedure for selection of UPAT-binding proteins. (B, Right) Lysates from HCT116 cells transfected with UPAT along with HA-tagged UHRF1, CDC27, hnRNPU, UBTF, or VCP were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody followed by RT-PCR analysis to detect UPAT mRNA. GAPDH mRNA and U1 small nuclear RNA were used as negative controls. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (C) Lysates from HCT116 cells transfected with HA-UHRF1 were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody followed by RT-PCR analysis to detect UPAT mRNA. GAPDH mRNA, U1 small nuclear RNA, ASBEL, and UCA1 were used as negative controls. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (D) Lysates from HCT116 cells transfected with Flag-UHRF1 along with UPAT or AOC3 were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody followed by RT-PCR analysis to detect UPAT or AOC3 mRNA. U1 small nuclear RNA was used as a negative control. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (E) Lysates from HCT116 cells that had been transfected with UPAT and the indicated HA-UHRF1 (Left) or Flag-UHRF1 (Middle and Right) deletion fragments were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA (Left) or anti-Flag (Middle and Right) antibody followed by immunoblotting analysis with anti-HA or anti-Flag antibody. (F) Lysates from HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting UHRF1 were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-UHRF1 or anti-Actin antibody. Actin was used as a loading control. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of UHRF1, SCD1, and SPRY4 expression in CCSC#P cells transfected with siRNA targeting UHRF1. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (H) Annexin V assays were performed with HCT116 cells that had been transfected with siRNA targeting UHRF1. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05. (I) qRT-PCR analysis of UHRF1 expression in human colon cancer tissues (n = 17 pairs). *P < 0.05. (J) UHRF1 is not required for the expression of PGM1 and GPRC5A. qRT-PCR analysis of PGM1 and GPRC5A expression in HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting UHRF1. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (K) ChIP assays were performed with HCT116 cells transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting UPAT using anti-UHRF1 antibody. GAPDH-transcription start site (TSS), SPRY4-TSS, and SCD1-TSS are derived from the TSS of the GAPDH, SPRY4, and SCD1 genes, respectively. GAPDH-TSS was used as a negative control. *P < 0.05. (L) HCT116 cells transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting UPAT were treated with Actinomycin D for the indicated times and then subjected to qRT-PCR analysis of SCD1 expression. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (M) Schematic representation of the SPRY4 locus. (N and O) hMeDIP–qRT-PCR (Left) or MeDIP–qRT-PCR (Right) assays were performed with the HCT116 cell transfected with control siRNA or siRNA targeting UPAT (N) or UHRF1 (O) using anti-5hmC (Left) or anti-5mC (Right) antibody. SFRP1 was a positive control for 5mC. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 2). *P < 0.05. (P) qRT-PCR analysis of TET1 and SPRY4 expression in HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting TET1. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 2). (Q, Upper) qRT-PCR analysis of DNMT1 expression in HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting UPAT. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). (Q, Lower) Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-DNMT1 or anti–α-tubulin antibody. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. (R) Dot blot analysis of genomic 5mC in HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting UPAT. (S and T) HCT116 cells transfected with siRNA targeting UPAT were subjected to immunoblotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. Actin and α-tubulin were used as loading controls.