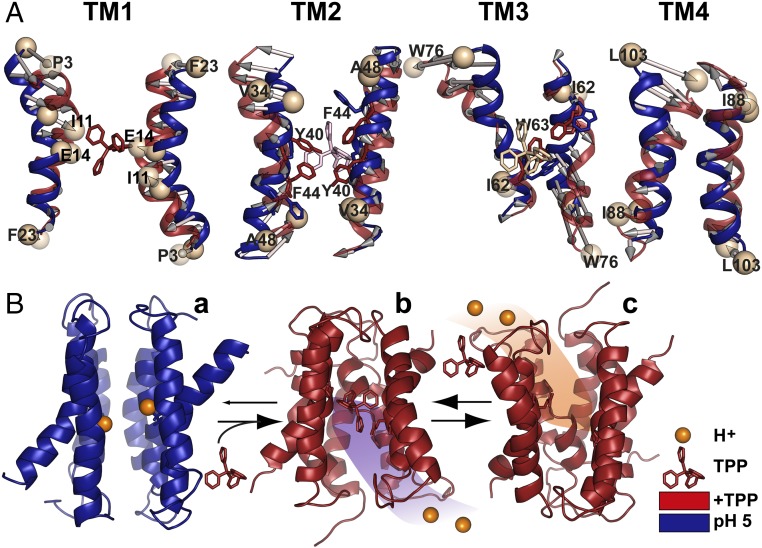
Fig. 6.
Model of EmrE transport derived from EPR data. (A) Conformational changes between protonated (pH 5) and TPP-bound intermediates. Overall alignment between respective TM pairs is shown; for TM3, alignment was based on residues 58–64. (B) The resting state is a protonated but water-occluded conformation of EmrE, represented here with the symmetric model generated by BCL::Fold/Rosetta and refined in MODELLER by pH 5 distance restraints (a). Subsequent binding of the substrate from inner membrane leaflet promotes release of the protons, yielding the refined TPP-bound crystal structure (b). Conformational exchange of the monomers enables alternating access to the extracellular milieu, and exchange of substrate with protons resumes the cycle (c).