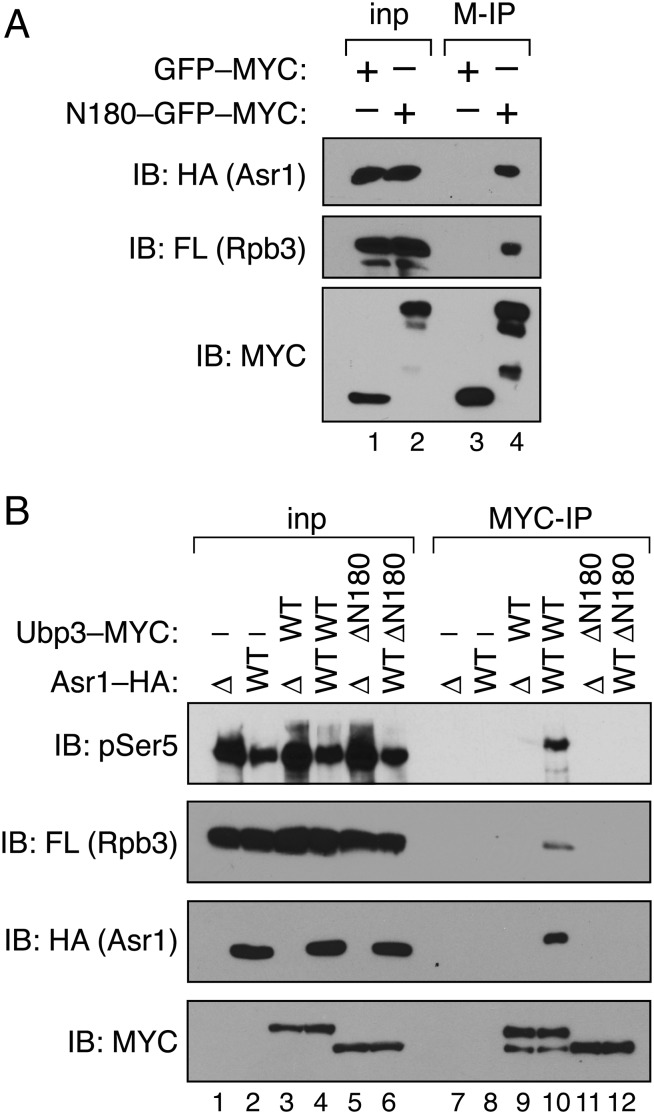
Fig. 3.
Interaction of Ubp3 with RNA polymerase II is mediated via Asr1. (A) The amino terminus of Ubp3 suffices for interaction with Asr1 and pol II. Extract was prepared from cells expressing HA-tagged Asr1, FLAG-tagged Rpb3, and either MYC-tagged GFP alone (YTM43), or MYC-tagged GFP fused to the amino-terminal 180 residues of Ubp3 (YTM42). Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with an anti-MYC antibody (M-IP), and products were subjected to immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA, -FLAG, and -MYC antibodies. For Rpb3–FLAG and Asr1–HA, 2.5% of the input was analyzed; for Ubp3–MYC, 0.1% of the input was analyzed. (B) Ubp3 requires Asr1 to interact with pol II. Extracts were prepared from yeast expressing FLAG-tagged Rpb3, and carrying combinations of (i) an ASR1 gene deletion (∆) or expression of WT HA-tagged Asr1, and (ii) WT MYC-tagged Ubp3 (WT) or the ∆N180 MYC-tagged Ubp3 mutant (lanes 1 and 7, YTM21; lanes 2 and 8, YTM22; lanes 3 and 9, YTM23; lanes 4 and 10, YTM24; lanes 5 and 11, YTM25; lanes 6 and 12, YTM26). IP was performed with an anti-MYC antibody (MYC-IP), and products were subjected to IB with anti-pSer5, -FLAG, -HA, and -MYC antibodies. For pSer5, Rpb3–FLAG, and Asr1–HA, 2.5% of the input was analyzed; for Ubp3–MYC, 0.1% of the input was analyzed.