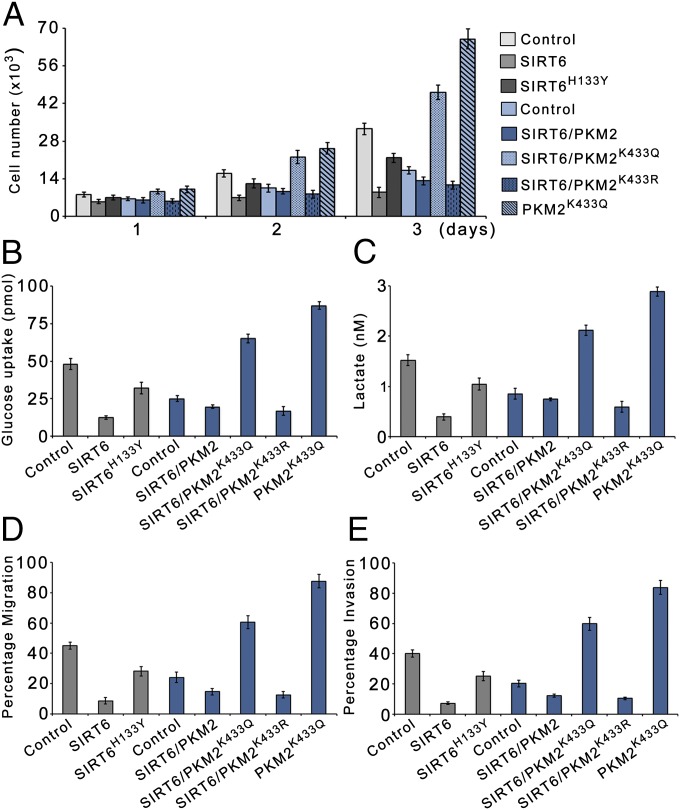
Fig. 6.
SIRT6 suppresses PKM2-dependent cell proliferation and malignant phenotype. (A) HepG2 SIRT6kd cells (gray bars) or SIRT6/PKM2 double-knockdown cells (blue bars) were stably transfected (pooled hygromycin-resistant population) with a dual expression plasmid encoding FLAG-tagged wild-type SIRT6, FLAG-tagged SIRT6H133Y, PKM2K433Q, and FLAG-tagged wild-type SIRT6 along with PKM2K433Q or PKM2K433R as indicated. HepG2 SIRT6kd or SIRT6/PKM2 double-knockdown cells stably transfected with empty vector served as control. The cells were harvested and counted at the indicated time points. Error bars represent means ± SD of three independent experiments with duplicate samples. (B) The glucose uptake of the cells in A was measured. Error bars represent means ± SD of three independent experiments with duplicate samples. (C) The lactate production of the cells in A was measured. Error bars represent means ± SD of three independent experiments with duplicate samples. (D) The migration potential of the cells in A was measured as the percentage of cells migrating to the bottom chamber. Error bars represent means ± SD of three independent experiments with triplicate samples. (E) In vitro invasion of the cells in A was measured as the percentage of cells migrating to the bottom chamber. Error bars represent means ± SD of three independent experiments with duplicate samples.