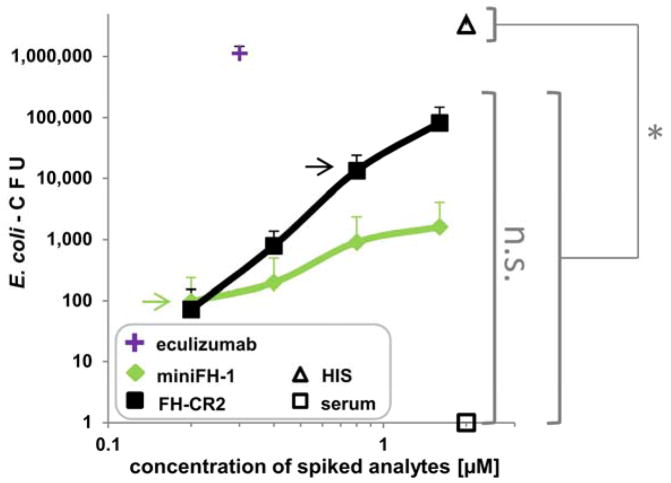
Figure 4. Complement mediated killing of E. coli in NHS.
E. coli cells containing a selective marker were incubated for 1h in NHS spiked with complement inhibitors or PBS. Colony forming units (CFU) were evaluated by colony counting after plating the reactions on selective medium. Eculizumab was used at 0.3 μM, which nearly corresponds to the known human C5 plasma conc. of 0.38μM (HIS: heat inactivated serum; average of 3 assays with SD is shown, except for eculizumab which was assayed only twice). Selected points were analyzed for significant changes in CFU (non-parametric one-way analysis of variance with a significance level of p < 0.05; GraphPad Prism). The number of CFU of the serum control and the two selected concertation points of the targeted inhibitors that fully protected PNH erythrocyte hemolysis (0.2 μM miniFH-1 (green arrow); 0.8 μM FH-CR2 (black arrow)) were significantly smaller (*) than the number of CFU for heat-inactivated serum. No statistical significant (n.s.) change was noted between the serum control and the concentration points of miniFH-1 and FH-CR2.